$20 Bonus + 25% OFF CLAIM OFFER
Place Your Order With Us Today And Go Stress-Free
Summative Assignment – Research Proposal
The assignment for this unit has been designed to give all students the opportunity to prepare a document demonstrating their ability to produce a coherent, theoretically based argument justifying research within a specific field. The development of such documentation is not only one of the essential skills of the postgraduate student; it is a key requisite for policy planning and project work. The format for this assignment whilst individual to this institution provides a baseline that can be used to help develop protocols in the future.
Remember this assignment is basically a statement of intent; it should present a clear picture of what is planned and why the project is worthwhile. Although not all issues will be studied and researched in the same way there are some features that need to be in them all, and the following guidelines have been devised to help in the preparation of the assignment.
Telehealth techniques have shown great potential as an alternative to in-person consultations. The delivery of mental health therapies has shown potential with technology in healthcare (Zhou et al., 2020). It offers several advantages, including greater accessibility, comfort, and effectiveness.
Although telehealth has enormous promise for enhancing mental health treatment in the UK, several roadblocks include a dearth of adequate infrastructure, security, privacy concerns, and the potential for unequal internet access. This study aims to perform a thorough literature analysis on the usage of telehealth in the UK for the treatment of patients with mental health concerns.
This study will look into the benefits and drawbacks of telehealth, the evidence for its efficacy, and the barriers to its general adoption.
Due to the high prevalence of mental illness, the United Kingdom has a significant issue in terms of public health. According to McCellan et al. (2020), one in four people will experience a mental health condition at some point in the year. Only a few of the numerous economic and societal effects of mental health problems include lost productivity, increased healthcare consumption, and diminished quality of life.
The COVID-19 outbreak has led to an increased prevalence of mental health issues. As a result, telemedicine therapies have become a potential alternative to face-to-face consultations in the mental health industry.
Telehealth treatments are helpful in the treatment of mental health problems, according to studies. In order to assess the effectiveness of telepsychiatry in treating a range of mental health issues, such as depression, anxiety, and post-traumatic stress disorder, Veazie et al. (2020) did a systematic review and meta-analysis. Telepsychiatry can reduce the workload for healthcare professionals and boost patient satisfaction, according to this investigation.
Another essential document in this field is the United Kingdom's Department of Health's "Five Year Forward View for Mental Health" (Dawson et al., 2020). This essay emphasised the significance of improving access to mental health therapies, pointing to technological innovation and creative thinking as the main drivers of progress.
In particular, the report emphasized the significance of telehealth activities in enhancing healthcare access for marginalized populations.
The UK cannot fully take advantage of telehealth for mental health therapy due to several obstacles. After a thorough investigation, Shigekawa et al. (2018) identified several barriers to the broad use of telepsychiatry, including a lack of adequate infrastructure, concerns about data privacy and security, and the potential for unequal access to technology.
Research (Jacobs et al., 2019) shows that telemedicine techniques can be as successful as in-person consultations. Several challenges must be addressed to ensure that everyone has equitable access to medical care before they can be implemented.
Also Read - Nursing Assignment Help
The aftermath of the COVID-19 epidemic has highlighted the urgent need for fresh ideas to increase access to mental health treatment in the United Kingdom (Patel et al., 2020). The increased need for mental health services due to the pandemic's broad disruption demonstrates the stress on the healthcare system. In this context, telehealth strategies have shown promise as a substitute for in-person consultations with healthcare professionals.
Telehealth programs may increase access to mental health services. However, there are still obstacles to their broad usage. A significant barrier is inadequate facilities and equipment (Wilson et al., 2017).
The broad acceptance of telehealth practices depends on technology like wearable monitoring, digital health records, and secure video conferencing systems. The broad implementation of such technology requires integration into current healthcare systems and strict adherence to privacy and security regulations.
Inequalities in access to technology may also exist, which might be problematic for underprivileged communities (Lurie and Carr, 2018). The availability of and familiarity with digital technology among the populace is crucial to the success of telehealth initiatives.
Due to a lack of access to the necessary equipment or a lack of digital literacy, some patients might not be able to benefit from telehealth consultations (Pfender, 2020). The goal of this study is to thoroughly examine how successfully telehealth therapies are assisting patients in the UK who are struggling with mental health difficulties.
In order to alleviate the scarcity of mental health care in the United Kingdom, this study aims to evaluate the effectiveness of telehealth initiatives. The COVID-19 pandemic's aftermath has made it much more crucial to develop new solutions to the already severe mental health issue and the associated burden on the healthcare system, as North (2020) notes.
The study results will aid policymakers and medical specialists understand how telehealth treatments may enhance the standard of care for persons in the UK dealing with mental health difficulties. The study's results will strengthen the body of evidence supporting the use of telehealth to improve patient outcomes, cut healthcare costs, and increase patient access to treatment. This study will highlight topics that need more research in addition to filling up any gaps in the existing literature.
In order to better assist persons with mental health concerns, policymakers and service providers in the UK may use the study's findings. The study's findings will provide insight into the benefits and drawbacks of telehealth therapy for people with mental health conditions. The study aims to identify the barriers preventing the widespread adoption of telehealth practices and to offer solutions.
The study results will be disseminated through conventional academic channels, including peer-reviewed publications and conferences. The research findings will advance the understanding of telehealth therapies and how they could increase access to mental health services in the UK. The study's findings will interest researchers, decision-makers, and professionals in the mental health field.
Also Read - Human-Centred System Design
The researcher acquired a substantial body of literature and research papers from the academic database Google Scholar to examine the information that other researchers have accumulated on this subject. The study's primary and secondary sources were academic databases, official records, and statistics reports.
"The Current State of Telehealth Evidence: A Rapid Review" by Shigekawa et al. (2018) critically reviews the current telehealth literature. The main subjects of this study include telehealth treatments' efficacy and viability, as well as the challenges of putting them into practice. In order to synthesise knowledge on a specific topic, the authors used a systematic review technique for data collecting (Shigekawa et al., 2018).
They searched through numerous databases to choose the most pertinent publications and used strict inclusion criteria. This article provides a helpful overview of the current telehealth research. Shigekawa et al. (2018) underline the need for further research, particularly more significant studies with more extended follow-up periods and more rigorous study designs, to address the gaps in the present data set.
Perry, Gold, and Shearer's (2019) study aimed to identify and address the barriers that mental health professionals believe prevent them from utilising clinical video telehealth. The authors combined survey data with follow-up interviews to reach their results. The survey gathered data on the respondents' origins, familiarity with telehealth, and the difficulties they could face.
The interviews aimed to dive more deeply into the challenges that the survey indicated and to elicit suggestions for accelerating telehealth adoption. According to the findings, the most often reported reasons for not adopting telehealth were technical challenges, concerns about the effectiveness of the care, and concerns about how telemedicine would influence the therapeutic alliance. It is also important to highlight that older doctors with more telemedicine experience reported fewer obstacles to telehealth utilisation.
The results of this study help direct efforts to expand the use of telehealth by mental health providers (Perry, Gold, & Shearer, 2019). Despite these limitations, the study does close a knowledge gap on how mental health experts see the application of telehealth.
In light of the research by Perry, Gold, and Shearer (2019), it is crucial to address clinicians' concerns about technological difficulties and how telehealth affects the therapeutic relationship. More research is required to understand better the potential and problems that telehealth's expanding usage in the mental health treatment field presents.
In their work titled "The Role of Telehealth in Reducing the Mental Health Burden from COVID-19," Zhou et al. (2020) explore the possibility that telemedicine might assist in reducing the psychological discomfort brought on by the COVID-19 pandemic. The authors discuss the difficulties of providing mental health care face-to-face and how telemedicine may help with these problems.
They contend that telehealth can increase access to mental health care while making it more flexible and less stigmatising. The authors also discuss the cognitive-behavioral model, the social support theory, and the stress and coping theory as theoretical underpinnings of telemedicine in mental health therapy. These theories suggest that telemedicine treatments mitigate the psychological effects of COVID-19.
The authors employed a thorough literature review methodology to investigate the utilisation of telemedicine for mental health therapy during the COVID-19 epidemic (Zhou et al., 2020). In order to discover studies that assessed the value of telemedicine in providing mental health treatments during the pandemic, researchers searched through digital libraries. The authors synthesised a narrative and evaluated the research critically.
Despite the study's thorough review of the literature on the use of telemedicine for mental health care during the COVID-19 outbreak, some essential points remain. First off, as the study solely considers the COVID-19 pandemic, it needs to be clarified how generalizable the findings are. Second, the included research differs in quality and consistency, which might reduce the overall strength of the review's conclusions.
The authors should have assessed the potential drawbacks of telemedicine for treating mental illness, such as the absence of nonverbal cues and probable technical difficulties. The study, as a whole, provides insight into how telemedicine could lessen the psychological effects of COVID-19 (Zhou et al., 2020). Additional research is necessary to assess the effectiveness of telehealth therapy in diverse mental healthcare settings and to address potential restrictions and detrimental effects.
In his article "Using Telehealth to Remediate Rural Mental Health and Healthcare Disparities," Myers (2018) examines the potential of telemedicine in addressing disparities in mental health treatment for rural populations. This article critically analyses the literature on the use of telehealth in rural areas, focusing on the information and concepts offered as well as the methods utilised to get the information.
The author contends that telemedicine can reduce the disparity in mental health outcomes between rural and urban areas by increasing access to care in disadvantaged regions. Although the article emphasises the advantages of telehealth in rural areas, it also acknowledges the drawbacks, including a lack of dependable internet and needing more doctors with the necessary skills.
This essay reviews the pertinent literature and bases its arguments on several sources (Myers, 2018). The author also critically assesses the data and theories presented in the literature, highlighting their shortcomings and limitations.
According to the paper, many studies on telehealth in rural areas have used self-reported data or small sample sizes, which may limit the generalizability of the results. The author also suggests more rigorous approaches, such as randomised controlled trials, to assess the effectiveness of telehealth treatments in the future.
Also Read - Analysis Of Strategic Event Tourism Dubai
The following are the primary research questions for the study:
What is the effectiveness of telemedicine in improving mental health outcomes for people with known mental health issues compared to traditional face-to-face treatment?
What impact does telehealth use have on the accessibility of mental health services in underdeveloped and distant areas?
What are the benefits and drawbacks of telehealth for mental health treatment that doctors and patients should be aware of?
How may telemedicine be more effectively incorporated into the present mental health care systems to improve patient care and outcomes?
What privacy, confidentiality, and informed consent issues do the usage of telehealth raise about mental health treatments?
Since the researcher will be doing this inquiry utilising secondary qualitative methods, there will not be a hypothesis.
The proposed study aims to investigate how telehealth usage has affected the equality and accessibility of mental health care for underrepresented populations. The study employs a qualitative technique and a thorough literature review to identify gaps in knowledge and inconsistencies.
This approach is consistent with a constructivist epistemology (Iovino and Tsitsianis, 2020), which acknowledges the importance of context and subjective perspective in knowledge creation. The social determinants of health idea, which recognises the interaction between socioeconomic position and environmental factors affecting health status, serves as the study's broad theoretical framework.
The research will use a systematic review technique to gather information from previously published studies on the issue of telehealth's application to the delivery of mental health care for disadvantaged persons (Sileyew, 2019).
The basis for the review will be a thorough search strategy using several internet databases, grey literature, and research reference lists. By identifying themes in the articles, the researcher evaluates and examines their connections; the researcher will gather and analyse data using a thematic synthesis technique.
The researchers decided to perform a systematic review of the pertinent literature to gather data regarding the use of telemedicine to lessen mental health disparities in rural areas. A systematic review consists of a thorough search, critical evaluation, and synthesis of pertinent information (Pandey & Pandey, 2021).
This approach is appropriate for this study because it enables a full assessment of all pertinent data, including qualitative and quantitative research. The systematic review will follow a specified process to ensure the search strategy is open, reproducible, and objective.
The kind of telehealth intervention, the target population (rural residents with mental health concerns), and the study's primary goals (mental health outcomes, access to care, and healthcare disparities) will all be considered when determining whether a participant is eligible for the study.
Both automatic and human methods are part of the search approach. There will be databases like PubMed, Embase, and PsycINFO included in the automated search.
The following inclusion and exclusion criteria apply to the current study:
| Inclusion criteria | Exclusion criteria |
|
|
The present study technique is secondary and qualitative. Thus, there is no need to create a new instrument for data collection. Instead, the researcher will rely on already-existing data sources such as academic journals, reports, and databases. The researcher will thoroughly study the literature to identify the best data sources. The review would follow the accepted practices for such systematic reviews to ensure reliable outcomes. Using qualitative methodologies, the researcher will look for patterns and trends in the collected data. This will enable the researcher to offer a thorough analysis of the potential of telehealth to address healthcare and mental health disparities in rural locations. The investigation will also assist the researcher in identifying gaps in the existing body of knowledge and identifying potential new research areas.
Any academic investigation must take dependability and validity into consideration. Reliability is the idea that a data collection tool should consistently produce the same results. On the other hand, validity refers to how accurately the data collection instrument measures the relevant variables. This study will assess the reliability and validity of the secondary sources employed to ensure the data's consistency and correctness. You will need to evaluate the validity of your sources during this process and search for any indications of bias or limitations. Using accepted criteria for evaluating qualitative research projects, the researcher will also analyse the validity and reliability of the data. If the study's validity and reliability are guaranteed, its findings will be reliable and credible, potentially influencing healthcare policy and practice.
The proposed study would gather and analyse data using qualitative approaches, namely theme analysis. The analysis will involve identifying and making sense of data trends and dissecting overall themes into more complex ideas. This approach makes it feasible to extract pertinent data and develop a complete understanding of the topic under research (Iovino & Tsitsianis, 2020). In order to check the data's veracity and correctness, there will be several iterative sweeps over the data. Results must be presented narratively, with descriptive language and quotes from the data to support them. The objective is to provide a complete description of the phenomenon and to draw conclusions from the research.
When conducting public health research, it is vital to protect the rights and well-being of study participants. The ethical principles of autonomy, beneficence, non-maleficence, and fairness are among the most crucial ones to consider in the research that is being planned. In order to respect participants' desires to participate in the study, researchers must safeguard their privacy. Additionally, researchers must ensure that the study's advantages outweigh the risks to participants and take all required precautions to lessen the possibility of harm.
This study will interpret the data provided by following the norms of the "Data Protection Act 2018" by adhering to the "Data Protection Act 2018," as well as by citing and referencing the work of other authors who have done comparable studies (Fraser et al., 2019). Additionally, researchers must choose participants fairly and reasonably without using any compulsion. The researcher must also maintain the security and privacy of the collected data. Researchers must obtain approval from an unbiased, ethical commission before starting the study. The committee will review the research proposal to ensure that all procedures, from participant recruitment to data analysis, comply with ethical standards.
Also Read - Clinical Reasoning Cycle
To sum up, the study's findings have significant consequences for public health. The findings of this study will advance the understanding of how effective strategies are at preventing childhood obesity. It is important to note that the initiative has its problems. Employing a secondary and qualitative research technique can constrain the depth of the examination. The validity of the findings might be impacted by the caliber of the primary studies used in the meta-analysis. However, the findings of this study will be very beneficial to those who decide healthcare policy and practitioners. Researchers recommend that future studies employ a mixed-methods approach to overcome the study's limitations and give a more comprehensive picture of how to treat and prevent childhood obesity.
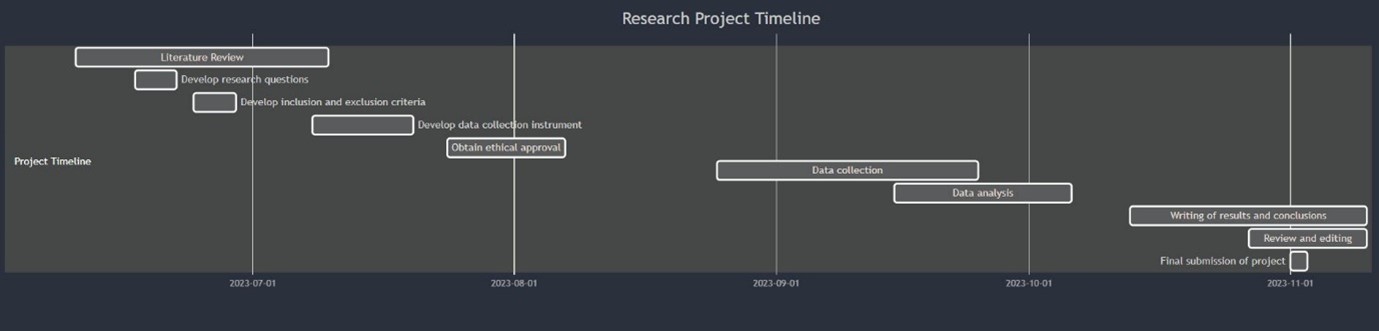
Figure 1: Research project Gantt chart
(Source: Researcher)
Finding Academic Literature: Using Google Scholar, the Internet, and a Computer
Dawson, A.Z., Walker, R.J., Campbell, J.A., Davidson, T.M. and Egede, L.E., 2020. Telehealth and indigenous populations around the world: a systematic review on current modalities for physical and mental health. Mhealth, 6.
Fraser, K.D., Garland Baird, L., Labonte, S., O’Rourke, H. and Punjani, N.S., 2019. Case manager work and workload: Uncovering a wicked problem—A secondary analysis using interpretive description. Home Health Care Management & Practice, 31(2), pp.83-91.
Iovino, F. and Tsitsianis, N., 2020. The methodology of the research. In Changes in European energy markets (pp. 79-95). Emerald Publishing Limited.
Jacobs, J.C., Blonigen, D.M., Kimerling, R., Slightam, C., Gregory, A.J., Gurmessa, T. and Zulman, D.M., 2019. Increasing mental health care access, continuity, and efficiency for veterans through telehealth with video tablets. Psychiatric Services, 70(11), pp.976-982.
Lurie, N. and Carr, B.G., 2018. The role of telehealth in the medical response to disasters. JAMA internal medicine, 178(6), pp.745-746.
McClellan, M.J., Florell, D., Palmer, J. and Kidder, C., 2020. Clinician telehealth attitudes in a rural community mental health center setting. Journal of Rural Mental Health, 44(1), p.62.
Myers, C.R., 2019. Using telehealth to remediate rural mental health and healthcare disparities. Issues in Mental Health Nursing, 40(3), pp.233-239.
North, S., 2020. Addressing students’ mental health needs via telehealth. North Carolina Medical Journal, 81(2), pp.112-113.
Pandey, P. and Pandey, M.M., 2021. Research methodology tools and techniques. Bridge Center.
Patel, S.Y., Huskamp, H.A., Busch, A.B. and Mehrotra, A., 2020. Telemental health and US rural–urban differences in specialty mental health use, 2010–2017. American Journal of public health, 110(9), pp.1308-1314.
Perry, K., Gold, S. and Shearer, E.M., 2020. Identifying and addressing mental health providers’ perceived barriers to clinical video telehealth utilization. Journal of Clinical Psychology, 76(6), pp.1125-1134.
Pfender, E., 2020. Mental health and COVID-19: implications for the future of telehealth. Journal of patient experience, 7(4), pp.433-435.
Shigekawa, E., Fix, M., Corbett, G., Roby, D.H. and Coffman, J., 2018. The current state of telehealth evidence: a rapid review. Health Affairs, 37(12), pp.1975-1982.
Sileyew, K.J., 2019. Research design and methodology (pp. 1-12). Rijeka: IntechOpen.
Veazie, S., Bourne, D., Peterson, K., and Anderson, J., 2019. Evidence brief: video telehealth for primary care and mental health services.
Wilson, F.A., Rampa, S., Trout, K.E. and Stimpson, J.P., 2017. Telehealth delivery of mental health services: an analysis of private insurance claims data in the United States. Psychiatric Services, 68(12), pp.1303-1306.
Zhou, X., Snoswell, C.L., Harding, L.E., Bambling, M., Edirippulige, S., Bai, X. and Smith, A.C., 2020. The role of telehealth in reducing the mental health burden of COVID-19. Telemedicine and e-Health, 26(4), pp.377-379.
Also Read - Science Assignment Help
Are you confident that you will achieve the grade? Our best Expert will help you improve your grade
Order Now