$20 Bonus + 25% OFF CLAIM OFFER
Place Your Order With Us Today And Go Stress-Free
This study aims to find out the contribution of social platforms to delivering the right data to the people to select an appropriate tourist location. This study described the consumer perceptions, in the case of selecting the favourite destination in India.
The content that is available on social media includes positive and even reviews which help the consumer to choose the right location which can best suit them. Some challenges of social media have been also described along with the recommended strategies to reduce those challenges.
This study includes primary quantitative data which can help the readers and future researchers to find authentic and error-free information. Descriptive research design has been used which helps to describe the evidence which is related to the impact of social media on the decision-making process of Indian tourists.
On the other hand, a deductive approach is used to analyse the perceptions of Indian tourists after inflicting the sinew that is published on social media. SPAA analysis has been conducted by the research team by analysing the survey responses to offer better ideas to the readers. Maintenance of ethics and protocol used to develop the quality of the overall study.
Social media is a part of the search engine optimization process where people can search for different kinds of information (Hartanto et al., 2022). As per the report of Basuroy (2022), there are 600 million people in India who are active users of social media. This indicates that they can easily get valuable information regarding tourist destinations from social media.
The purpose of this research study is to analyse the contribution of social media to illustrate customers perceptions and improve decisions for selecting the right tourism destination. This chapter has discussed the aim and objectives of the research study and illustrates the structure for conducting research. Besides, significant research has been discussed in this section to clarify the purpose of the research journey.
Social media platforms have a significant contribution to bringing large amounts of information that is impossible to physically search. It has been found that around 600 million people are engaged with social media to visit different kinds of search platforms for the adoption of knowledge (Basuroy, 2022).
Based on the information, it can be stated that the selection of the right tourism destination is another contribution of social media. In India, there are lots of historical and mythological tourist places present. By gathering information from social media tourists can choose their desired location or tourist spots.
Customer relationship management might be involved in social media where social media collect and store data in customer insight on social media sites (Wibowo et al. 2020). Besides, a two-way communication process is involved where the customers' perceptions are collected to review for understanding their demand.
In this way, social media provides the right information to customers by mentioning new additions. Social media platforms such as Facebook, YouTube and Instagram provide user-generated video and content, which includes travelling details and reviews.
Travel vloggers share the overall experience and facilities of that location by knowing that social media users can identify the budget and facilities of that place and select the tourism destinations (Armutcu et al., 2023). This study shed light on different areas which used to develop the decision-making orcas of tourists who want to visit the places of India.
Effective communication in social media builds a strong connection with the travel agents which can enhance the experience of a tourist. In this way, social media provides the right information by providing recent and trading content. The purpose of this study is to analyse the role of social media in convincing customers to select the right tourism destination with an analysis of their perceptions that are discussed below in figure 1.

Figure 1: Social media platform usage
(Source: Adgully, 2022)
The aim of the study is to understand the importance of social media platforms in selecting,
tourist destinations by potential customers in India.
● To identify the role of social media in selecting appropriate tourist destinations
● To recognise the impact of social media to influence the decision-making process of tourist.
● To evaluate the challenges of social media which affect the decision-making process of tourists to find the right lactation in India.
● To recommend strategies that travel companies can employ while using social to gain the attention of Indian tourist.
● What are social media platforms used for influencing the perceptions of tourists while selecting tourism destinations in India?
● What role do social media influencers play in affecting the perceptions of tourists in India?
● What are factors that affect the perceptions of tourists while selecting tourism destinations in India?
● What are the theories that can be used for explaining the link between perceptions of tourists and social media?
Hypothesis 1
H0: There is no significant correlation between individuals' proficiency in using social media platforms and the challenges they face in the context of social media and tourism in India.
H1: There is a significant positive correlation between individuals' proficiency in using social media platforms and the challenges they face in the context of social media and tourism in India.
Hypothesis 2
H0: There is no significant relationship between the professional status of individuals and their ability to overcome technical obstacles in utilizing dedicated social media channels for obtaining tourism information.
H1: There is a significant relationship between the professional status of individuals and their ability to overcome technical obstacles in utilizing dedicated social media channels for obtaining tourism information.
Hypothesis 3
H0: There is no significant association between participants expected future involvement in supplying tourism information through social media and their current assessment of each channel's ability to address technical issues.
H1: There is a significant association between participants expected future involvement in supplying tourism information through social media and their current assessment of each channel's ability to address technical issues.
Hypothesis 4
H0: There is no significant difference in the perceived effectiveness of specialized social media platforms among participants with varying levels of technical expertise.
H1: There is a significant difference in the perceived effectiveness of specialized social media platforms among participants with varying levels of technical expertise.
Hypothesis 5
H0: There is no significant relationship between different components extracted through PCA representing social media viewpoints and their association with tourism information variables.
H1: There is a significant relationship between different components extracted through PCA representing social media viewpoints and their association with tourism information variables.
The significance of the research study is to analysis about the role of social media in integrating customers' perceptions for making the right decision to identify the best tourist place. In the existing research papers, only the contribution of social media to the tourism industry has been discussed. This study shows that increasing presence on social media platforms help to change the tourism decision of the common people.
In India, there are several places that tourists love to visit, but increasing use of social media helps to increase the popularity of those places among many people (Armutcu et al., 2023). The social handles of travellers and bloggers are lots of images and videos which guide people to visit those Indian destinations.
The Tourism Ministry of India promotes historical places in social media which helps to draw the attention of a diverse group of people who are interested in historical places (Silaban et al., 2022). On the other hand, travel agents share the details of their tour packages on social media. This helps the customers to choose the right travel agency, so they can fulfil their needs and demands.
Social media is the place where different kinds of images, advertisements, and videos can be watched in one search. As per the opinion of Wright, (2021) Facebook, YouTube, Instagram, and Twitter are high customer engagement social media platforms.
The author said that to search for different content, these social media platforms use social media platforms to convince customers by delivering effective advertisements, sharing effective demographic content, and mentioning the right information regarding tourism facilities.
As per the opinion of Lara Setiati, and Ali (2019) transparency in business commitment is important for increasing the confidence of customers to buy products or services. Based on this information, providing trustable and transparent tourism sector services and destinations is essential for providing customers who understand organizational loyalty and selecting the right decision.
The Indian tourism industry is rapidly increasing which helps to extend the GDP rate each year. As per the opinion of Aftab, and Khan, (2019) social media platform is a cost-effective platform for travel agencies to update their service of tourism facilities. The author stated that a huge amount of information available on the social media platforms and reviews help new customers to more visits to sites to get details about the tourism destination.
In this way, social media collects customers' expectations to provide the best information to meet their needs. Around 44.5 per cent of social media users in India visit to see about tourism facilities and select the places. It can be stated that advanced technologies in social media might account for the number of visitors to tourism websites (Zak, and Hasprova, 2020).
It is a great scope for the tourism agencies in India to share advertisements of tourist places including effective content and graphical videos. In this way, social media convinces and attracts customers to be concerned about the given information to make the right decision.
As an example, MakeMyTrip provides weekly updates of tourism information on Instagram which helped to increase the follower rate to 190K. A trustable and cheapest service convinces customers to improve their travelling decision.

Figure 2: social media impact on tourism value creation
(Source: Longdom, 2022)
As per the opinion of Tang, and Liao, (2021), multiple information is available on social media that makes conflict situations to select the right decisions. The author stated that different kinds of positive and negative perspectives create complexity in making the right decision. These sequential cases have been seen in social media tourism platforms. Negative reviews and feedback regarding tourist places and services decrease the confidence of new tourists to make the right decisions.
Online communication such as social media chatting, sharing messages and queries must be required to be observed by travel agencies to provide the right decisions for selecting a tourism destination. On the other hand, Indian tourism is required to improve its service by observing negative reviews from old customers and providing the right and energetic commitment to convince new customers.
Also Read - Human Realtionship Management Assignment Help
In this present study, the primary quantitative method has been used to find out necessary information related to the present topic. The primary quantitative method is highly readable and authentic which helps to gain better outcomes using finding out the answers to the research question. Positivism philosophy has been used in these research studies to analyse the social impact and influence of social media for the identification of the right tourism destination (Govindarajo et al. 2018).
A deductive approach has been adopted in this research study to hypothetically examine the role of social media's positive and negative impact on Indian tourism and customer purchasing decisions. In this way, the right function of social media impact should be evaluated in the research study. The descriptive design has been adopted in this research study to explore the impact of social media platforms to influence the decision-making of tourists in India (Dey, and Das, 2019).
A primary research strategy has been used in this research to find and gain the updated information to understand the perception of Indian people regarding the benefit of social media for making the decisions while travelling in a place. SPPS used to analyse the collected data from the survey (Sivasubramaniam et al., 2021). This is used provide more detailed information regarding the point of view of survey participants.
During the data collection, maintenance of ethics used to develop the quality and maintain the transparency of the study. By notifying the participants before conducting the survey, the researcher guarantees the privacy and confidentiality of the data gathering procedure (Sivasubramaniam et al., 2021).
Before participating in the survey, participants were given the liberty to withdraw their consent at any time. Researchers share the purpose and motive of the study along with the benefits, and risks associated with the survey. This used to avoid the chance of miscommunication and confusion which used to find better results from the survey.
Chapter 1: Introduction
In this section, Aim and objective have been discussed in this section.
Chapter 2: Literature Review
In this section, the view of scholars' journals and articles has been executed to make a critical analysis of the research subject.
Chapter 3: Research Methodology
This section has discussed the methodological choices to make for this research to meet research objectives.
Chapter 4: Data Findings and Discussion
The data findings have been evaluated in this section to support for illustration of themes in the research study.
Chapter 5: Conclusion and Recommendations
An overall conclusion has been explained based on the research in this section with recommendations based on the improvement of challenges in using social media.
Figure 3: Dissertation structure
(Source: Created by the learner)
Social media plays a vital role in influencing the decisions of people when selecting any tourist destination. People can gather information regarding the tourist spots, locations, and transportation facilities of that particular area with the help of social media.
On the other hand, social media is used to build a communication network with different types of people which helps tourists to finalise the destination. Analysing the existing literature helps to recognize the decision-making process of Indian people while selecting any tourist destination. The below discussion helps to analyse the role of social media by providing accurate information which used to influence the decision-making process of Indian tourists.
Social media plays a significant role in influencing the travel decisions of Indian tourists due to the availability of different types of information. Indian people who love traveling and have a desire to visit new places are following the social influencers and their videos which inspire them to visit new places. Through social media platforms such as Facebook, YouTube, and Instagram people are getting tourist tips.
According to the point of view of Liu et al., (2020) by using social media platforms, Indian people are becoming aware of travel-friendly hotels and cheap tourist destinations. This influences middle-class people to fulfil their desire to visit new places.
The report of Gupta, (2022) stated that most of the people in India belong to the medium-income group so the use of social media platforms helps people to plan their cost-effective trips According to the report of Wong, (2023), there are 398.
Million Indian people who are in the age group of 18-19 using social media platforms. On the other 40.2% of people all over India use social media. This data shows that in the decision-making process of Indian people especially in the case of finalizing tourist destinations social media plays a crucial role.
Most of the people share their travel experience on social media or share videos on YouTube which influences other people to visit those places which works as an influential factor. As stated by Tham, Mair, and Croy, (2019), most travel agents are promoting their business on social media, which helps to draw the attention of most Indian people to those travel packages.
As per the viewpoint of Țuclea, Vrânceanu, and Năstase, (2020), Travel agents are promoting products and services on YouTube, Facebook, and Instagram which connect with the targeted group. For instance, Make My Trip, and Goibibo share weekly updates on Facebook and Instagram which include tourism and hotel booking-related information. This application provides easy hotel booking facilities to travellers. Effective hotel booking facilities encourage the desire of Indian People Who love to travel.

Figure 4: Role of social media to Encourage Travel Intention
(Source: Wang and Yan, 2022)
According to the above figure, it can be observed that social media provides prior knowledge to those people who are looking for suitable travel destinations. As observed by Wang and Yan, (2022), travel agencies are adopting a social media marketing strategy to recognize the travel indentation of customers.
Observing the above framework, it can be stated that the quality of information that Indian people get from social media is used to provide proper knowledge to them for enhancing their travel intentions. Through this, it can be stated that [roper knowledge from social media helps to plan a trip which can be budget friendly.
On the other hand, some hotels and resorts share their updates on social media, which helps the customer find a cost-effective hotel in their desired location. As substantiated by Thirumaran et al., (2021) social media is used to increase the business advantages of travel online travel platforms and travel agencies by sharing effective content and engaging videos. This helped to increase the desire among the common Indian people to plan to visit these tourist spots.
In India, there are a lot of historical and mythological tourist places such as Taj Mahal, Mysore place and Gateway of India. Watching content regarding these places helps to find actual information regarding those places which helps to grow the interest of the travellers. Most people share their journeys on YouTube or Facebook to encourage others, and that information influences the decisions of travellers (Werenowska and Rzepka, 2020).
According to the report of The Economic Times, (2023), more than 31% of people in India belong to the middle-income group, so they cannot afford any expensive tourist packages. Most of the travel agencies have their pages on Facebook, so customers can connect with the travel agents for better guidance.
According to the point of view of Armutcu et al., (2023) hotels and restaurants are adopting social media marketing and digital marketing strategies to connect with travellers or tourists which helps to recognize the tourist's intentions. Most Indian people belong to lower and medium-income groups, so they take much time to make tourist decisions.
They are using social media platforms to find effective information regarding accommodation, restaurants, and local tourist attractions before deciding on any location. In case booking any hotels near any tourist spots travellers go through the websites and check the comments of which help to make more informed decisions.

Figure 5: Impact of positive and negative reviews of social media
(Saini, Kumar, and Oberoi, 2023)
According to the above figure, it can be stated that Indian people depend on the reviews, and observing the positive and negative reviews helps to make better tourist decisions. Through this model, it can be stated that negative reviews on social media platform helps to increase awareness among Indian people so that they improve their traveller's plan by cross-checking the comment on different platforms (Werenowska and Rzepka, 2020).
On the other hand, the recommendation of social media influencers helps to reduce the confusion of the Indian people. They depend on the recommendations and suggestions of social media influencers who already visited some places of India. This is used to make cost-effective decisions. As the opinion of Saini, Kumar, and Oberoi, (2023) Content creators share experiences and opinions through which travellers can plan a hassle-free tour.
Social media not only helps to get the right information but also provides a wide range of travel-related facts that can draw the interest of travellers toward those destinations. As per the report of Sharma, (2023), it can be observed people of India prefer to watch travel content mostly which plays a crucial role in influencing their travel decisions. There are lots of travel destinations in India, and choosing the right destination among those is a difficult task.
Social media makes this task easier because it includes the details of every destination so that travellers can choose their favourite destination and get an idea of the total expenses. As per the viewpoint of Chatterjee and Dsilva, (2021), the tourism ministry of Odisha and Assam promoting sustainable tourism helps to draw the interest of the people to visit the tourist places of these two states. Thus, it can be stated that the positive impact of social media helps to increase the growth of the Indian tourism industry.
Tourism Ministry of different states of India promote their stated tourism on social media which is used to increase the traffic of tourists. According to the viewpoint of Idbenssi et al., (2023) The content that is shared on social media includes a variety of information that can help individuals to plan their trips as per affordability.
Due to the socio-cultural differences, the travel desires are different from each other. As supported by (Jangra, Kaushik, and Saini, 2021), social media provides diverse content for every group of users. On YouTube, they can search for desired content, which can guide them to plan a cost and time-effective trip. On the other hand, social media provides more captured information than traditional media.
Suer can easily find travel-related content on social media whenever they want, this is used to improve their decision-making skills. The government of India is taking the initiative to increase the popularity of tourists who are conscious about sustainability, so the government is collaborating with social influencers and celebrities to popularise tourist places in different states. Adaptation of digital marketing strategy by the government of Assam and Odisha used to promote sustainable tourist places to boost the tourism industry of those states.
Figure 6: Connection between social media and tourism decision
(Joo, Seok and Nam, 2020)
According to the above figure, social media influencers share their experience regarding their trips in rural areas and off-bit locations. Promotion of rural locations and tourist attractions can help to provide opportunities to the people who love to visit rural places of Rajasthan, and Gujarat (Joo, Seok, and Nam, 2020). Promotion of tourism services can be beneficial for travel agencies to find the target customers.
Along with this the promotional activities also help those people who are trying to find travel-related information in social media. The strong connection between social media and the tourist helps to make better decisions. According to the report of Hindustan Times, (2021), the Maharashtra government introduced tourism places to promote tourism activities after the global pandemic.
The government is taking initiatives to promote tourist places on social media platforms so that tourists can choose their desired location to fulfil their travel needs. Facebook and YouTube provide valuable resources for travelling, and Indian travellers can use those resources to collect information on different destinations.
As per the opinion of Santi and Fadjar, (2020) by using social media platforms such as Facebook, Instagram, and YouTube Indian tourists can communicate with the travel agent to get customized travel plans. By following the social media pages of hotels and resorts travellers can pre-book their hotels to avoid accommodation-related issues.
Through social media, government agencies, private agencies, and hotels increase the popularity of their products and services. For instance, the Tourism Board of Gujrat collaborates with film stars to promote their historical places to increase the traffic of tourists which influences consumer decisions.
A few years ago, the poor rural tourist places were not as popular as they are now. According to the opinion of Shang et al., (2021), in recent times with the help of social media, rural and offbeat palaces are gaining popularity, so that customers can choose rural places of India to experience the culture of rural India. On the other hand, the promotion of diverse cultures in India in social media is used to draw the interest of foreign travellers to visit the places of India.
In social media lots of information and images are available. People are getting confused after getting a variety of data, this can increase the challenges for travellers while finalizing a tourist destination in India. In India, different tourist places such as Kashmir, and the Himachal area are famous for the Hills and other places such as Goa and Andaman are famous for the sea beach. According to the point of view of Araceli Galiano Coronil et al., (2023), there is a lot of content available on YouTube where people cover those places.
Consumers find different tourist options which increase the confusion of the tourist to choose any place. Sometimes the information which is provided on social platforms is not true, which can increase difficulties for the tourist. As observed by Pop et al., (2021) Positive and negative reviews regarding any location are present in social media which creates a conflicting solution that affects the decision-making process of Indian and foreign tourists.
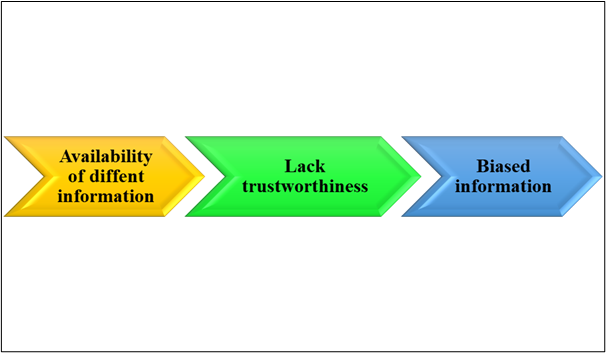
Figure 7: Disadvantages of making decisions by watching the content of social media.
(Source: Self-Developed)
According to the above figure, it can be stated that the point of view of different YouTubers is that common people are not able to find the right information so easily, which affects their process of travel planning. As stated by Hanaysha, (2022), all information that is present on social media is not trustworthy so finding the right travel agencies and travel agents is a difficult task for new travellers.
Due to increasing the business opportunities for paid promotion, YouTubers can share biased information and reviews which can cause of disappointment in the traveller. On the other hand, the popularity of a particular location in social media can increase the chance of over tourism which can increase the hassle of travellers. Promotional content that is shared on social media platforms cannot be effective for the consumers, through which consumers cannot get proper guidance from the knowledge and insights of social media.
The purchasing decisions of consumers such as travellers depend on the content that they have seen on social media. Before selecting any tourist spot in India, every tourist needs to understand the facilities of that place. According to the opinion of Werenowska and Rzepka, (2020), In such cases, effective communication with the travel agents can guide the travellers to make the right decisions.
Believing in the words of content creators can mislead the tourist, so before making any decisions reading the positive and negative reviews is very important. As stated by Faber et al., (2021), instead of depending on the information of content creators, tourists should gather information from the official Facebook page and websites of travel agencies. Before booking any hotels recommended by any social media influencer it is necessary to visit the official website of the hotel and go through the terms and conditions before booking.
When deciding on any place in India for travelling, lots of problems can arise, so tourist expectations should be realistic. Before visiting any state like Rajasthan or Gujrat, tourists should be aware of the transportation facilities of the area. As per the opinion of Sharifpour et al., (2018) Tourists should invest time in researching because the information that they get from the content creators can be biased. On the other hand, the expectation of everyone is not the same for everyone. Sharing a positive experience on social media regarding any place does not mean that everyone likes that place.
People should be aware of negative and positive facts related to the destinations. If the tourism industry promotes eco-friendly and sensible tourism it can offer opportunities to the people of India or foreign tourists to gain better travelling experiences. According to the point of view of Chia, Lee, and Han, (2020), in social media the concept of dark tourism is very popular, so one should be aware of the risks related to those places before visiting the dark places of India.
The points of view of people regarding the historical places of India are different, so tourists should find the right information to enjoy the beauty and culture of those places. If the social influencer shares the capital cost of the tour package it can be helpful for middle-class tourist to make their budget plan for the tour.
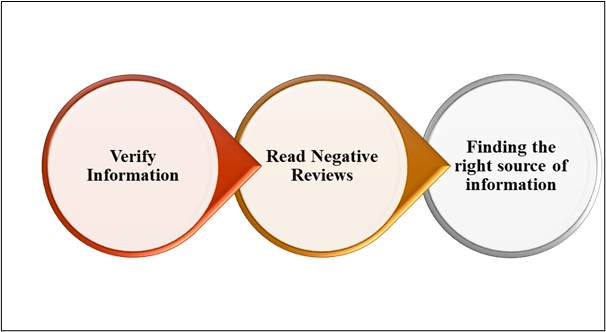
Figure 8: Strategies for reducing issues related to finding tourist destination.
(Source: Self-Developed)
According to the above figure, it can be stated that verifying the information that has been collected from social media can help to reduce tourism-related challenges. Observing the above figure, it can be described that verification of the information that Indian people get from social media helps them find out the truth and actual information. This will help them select a location through which they can fulfil their travel needs (Werenowska and Rzepka, 2020).
Reading the negative review can help to generate the idea of consumers, which is used to mitigate the upcoming challenges. The Tourism Minister of India can regularly share updates and promote eco-friendly tourism to provide a better travelling experience to tourists. Finding the right location for the tourist destination is a crucial task but finding authentic information from social media can reduce this problem. As observed by (Yuan et al.,2022), Consumers need to develop their research skills by analysing large amounts of videos and information available on different social platforms. In such a way consumers can make better decisions to decide their travel destination.
The present study explores the contribution of social media to deciding the travel destinations of Indian tourists. Application of theories helps to recognize different factors which are related to the experience of consumers. A discussion of different theories is described in the below section.
Figure 9: Application of Theories
(Source: Self-Developed)
Knowledge and understanding of Social Exchange Theory can help consumers to make the right decisions. While finalizing any tourist location in a country like India, tourists face difficulties so the components of this theory will work as beneficial factors to shape the decisions (Ahmad et al., 2023).
Referring to this theory can be analysed, observing the concept of this theory one can find the necessary information from social media to develop his tourism knowledge. Travellers have different expectations, and nurturing the knowledge of this theory helps them to set realistic expectations to get better experiences.
This theory can assist those people who are young and planning to travel to the attractive tourist spots of India, to make their tour plan more cost-effective by improving their knowledge. As per the knowledge of this theory, it can be described that consumers can gain proper knowledge regarding travelling (Zoller and Muldoon, 2019).
This can help them to compare the negative and positive reviews to find out the actual information from the social media platform. This theory influences the interpersonal skills of consumers so that they can make the proper decisions to enjoy their holidays in an attractive location in India.
Diffusion of Innovation Theory can work as a beneficial factor in developing the ideas and knowledge of Indian tourists and travellers. According to this theory, it can be analysed that people who are active on social media platforms can gain knowledge of information verification through this they can verify the collected information which can play a vital role in deciding the tourist place (Al-Razgan et al., 2021). This theory consists of 5 steps, the first stage is knowledge, so understanding the major components of this theory will help to increase the knowledge of common people who plan to visit unique places in India.
The second stage is persuasion, which helps the travellers to pause their passion for travelling. The third and fourth steps are decision and implementation which help develop the decision-making skills of travellers by collecting valuable data from social media platforms (CFI, 2022). The implementation step helps to implement the plans of travellers which can provide mental peace to them. The last step is confirmation (Silaban et al., 2022).
At this stage, tourists can be confident in the decision which can provide them with better travelling experiences (Faber et al., 2021). This theory is used to analyse the sentiments and feelings of consumers who are looking for the right information regarding their desired tourist spots (Araceli Galiano Coronil et al., 2023). The knowledge and understanding of this theory help them to develop their research skills to make sustainable and effective decisions.
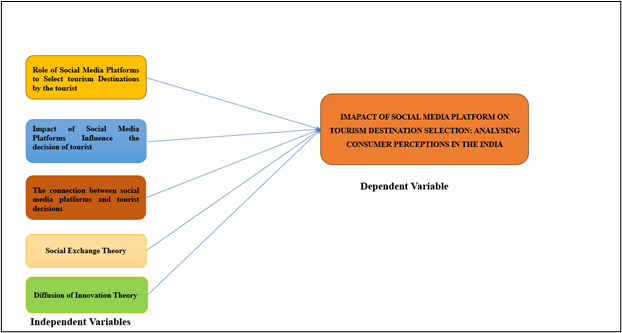
Figure 10: Conceptual Framework
(Source: Self-Developed)
Analysis: By observing the above conceptual framework, it can be identified that the role of social media is very significant in delivering relevant and up-to-date information to customers regarding travel and tourism. Common people are easily influenced by the words of content creators and social influencers (Armutcu et al., 2023). This study shows that there is a deep connection between social media and the decisions of tourists (Araceli Galiano Coronil et al., 2023).
The location covered by the YouTuber or the place that is trending on social media helps the people of Indian or foreign tourists to visit the same place. This is used to mitigate their desire to travel (Faber et al., 2021). Discussion of “Social Exchange Theory” shows the importance of social media platforms to develop the knowledge and decision-making skills of consumers.
Along with this “Diffusion of Innovation Theory '' helps to observe different stages of innovation that can be used to develop the interpersonal skills of the consumers for enhancing their knowledge of decision-making. The dependent variable is the “impact of social media platforms on tourism destination selection” which shows a deep connection with the independent variable such as the decision-making process of travellers who belong to India (Werenowska and Rzepka, 2020).
On the other hand, it shows a deeper connection with social exchange theory which helps to increase awareness among the people through social media to improve the travelling knowledge of Indian people.
This present study deals with the function of social media that is used to provide the idea of attractive tourist locations in India to consumers. The researcher found significant gaps in this study, due to the limited source of information. There is a lot of information available on the internet that deals with the contribution of social media platforms to influence travel decisions.
There are many published studies which help to measure consumer perceptions about destination selection. (Álvarez-García, Durán-Sánchez and del Río-Rama, 2018). There are limited sources present which can offer the idea regarding the impact of social media which used to influence the decision of travellers to choose tourist destinations (Imran et al.,2021). Due to the lack of significant information significant gap has been created.
The researchers try to find out the necessary data from published journals and news articles to include the necessary evidence which helps to find out the impact of social media to select the right tourist destinations in India (Faber et al., 2021). Through available information, researchers are ablaze to montage the significance of the literature.
Analysing the overall discussion, it can be summarised that social media is working as an effective to deliver a wide range of information. For people who are consumers and cannot fix any place they want to visit, videos and photos can resolve their confusion.
Different travel agencies, hotels, and restaurants are promoting their services on social media, so customers can easily connect with them to reach their dream destination in India.
YouTube videos offer travel tips and feedback from different people which guides the Indian tourist to select the right destinations. In the end, it can also be stated that consumers need to develop their research skills otherwise they can be misguided by the wrong information, available on Facebook, Instagram, and YouTube.
This chapter helps to provide ideas of different stages of research through which research can be conducted systematically. This chapter shows the ideas of appropriate research design methods and philosophy. This is used to find out the relevant data related to the impact of social media on influencing the decision of tourists towards choosing the right tourist destination (Jamil et al., 2022).
On the other hand, the adoption of an appropriate research philosophy is used to develop the quality of the study. This appropriate research design has been chosen to organise the data to find out the necessary information related to the given topic. Social media platforms such as
Facebook and YouTube are the focus of quantitative data analysis, which is used to assess their impact.
This study attempts to establish the most important features that can substantially improve decision-making capabilities among Indian visitors (Werenowska and Rzepka, 2020). On the other hand, this chapter views as crucial to maintain ethical standards to get objective data from the survey respondents. This information was then used to improve the overall quality of the study.
Provision of a research timetable assists the researcher to manage and execute the research in an efficient way within a given period. 2023) This chapter acts as a guide for researchers in choosing appropriate methods and processes to measure the impact of social media on traveller’s ability to locate suitable tourism destinations. In contrast, the review of ethics assists in identifying whether the researcher has indeed complied with laws and regulations to maintain the honesty and integrity of an overall study.
In the present study, the positivist research philosophy has been used to interpret the primary quantitative data. This philosophy helps the researchers to understand the topic and evaluate the collected data to recognise effective strategies (Žukauskas, Vveinhardt and Andriukaitienė, 2018). This physiology helps to find accurate data and information which can help Indian travellers select the right tourist destination. In addition to this, it can be stated that this study is based on primary quantitative, so the application of philosophy used to guide the researcher to include valuable evidence to identify the influence of social media on Indian travellers.
This philosophy also helps to analyse quantitative data from 115 participants by asking 13 close-ended questions. This used to find various opinions of the participants which can be appropriate to find the answers to the research question. Selection of this philosophy is used to evaluate the data which helps to understand the inventions of travellers by observing their presence in social media.
On the other hand, an adaptation of this philosophy is used to enhance the experience of the researcher to develop the quality of the research to guide the readers to select the right data and evidence. In this study Positivism research philosophy has been chosen to make the study unbiased and fulfil the strategic objective of this study. This philosophy allows the researcher to conduct a more impartial analysis of the topic to identify the influence of social media on the choice of tourism destinations in India.
In this study, deceptive research design has been used to describe the interpretation of numerical data. Researchers could use this research method to select the most appropriate questionnaires for survey designs that would look into the beneficial and detrimental effects of using social media platforms to decide whether or not to visit India (Gupta, Manohar Sajnani & Gowreesunkar, 2023).
This study utilised a research design that involved sorting out the collected data and performing statistical analysis to determine patterns and correlations between the variables and responses from the survey participants (Schiavenato & Chu, 2021). One of the purposes of using a descriptive research design is to describe phenomena in greater detail and evaluate the importance of correlations between variables.
This approach is used by researchers to organize the survey responses obtained from 115 participants. This is used to come up with hypotheses for more favourable results. For instance, theories can be applied to explain this research design to understand how often social media activity contributes to the decision of travellers with regard to choosing Indian tourism destinations (Liu et al., 2020).
To clarify, the data that has been collected has gone through a process of sifting to boost the validity of the hypothesis and survey findings by employing this specific methodology. In quantitative research, descriptive design is used to organize the responses from surveys and analyse them in a systematic manner. The use of this design enables the researcher to formulate the hypotheses.
The empirical investigation of the current study applied a deductive approach that aimed at making an emphasis on the formation of a hypothesis to identify the connection between one dependent and one independent variable. This research methodology is used to determine how social media platforms impact the decision-making of Indian travellers when choosing their potential tourist spots (Agyapong and Yuan, 2022).
On the contrary, the key purpose of this method is to realize access to fundamental qualitative data. This methodology is used to determine the main factors that play a significant role in influencing Indian traveller’s decision-making behavior who make use of social media platforms.
This methodology is focused on the development of hypotheses associated with answers received from the set of 115 survey participants, who work in the tourism industry and prefer using social media to find appropriate tourist spots (Abutabenjeh and Jaradat, 2018).
Using a deductive strategy, the study carefully analyses quantitative data to determine the necessary facts needed to know whether Indian traveller’s perception is being formulated or not. (Mosley and Biernat, 2020) The deductive approach apply statistical analysis to increase the rigor of research that depends on quantitative data following.
This technique is critical in order to achieve the goals and improve researchers’ qualification. Quantitative research provides detailed information about participants’ experiences and a deductive method helps researchers to test definite hypotheses and make conclusive results.
The study used the deductive approach to identify particular information from general information through the survey participants’ answers (Kim, 2021). After establishing a strong hypothesis, the researcher studies what the respondents are thinking by studying their travels on social media platforms and tracking their travel decision journey.
Figure 11: Benefits of using a Deductive approach
(Source: Kim, 2021)
A primary quantitative data was used to determine the effects of social media and opinions of Indian travellers. Primary data collected through a survey of 115 respondents were analysed to understand how they see travel in India. Primary quantitative data, on the other hand, provides a wide range of reliable and unbiased information. 115 individuals were taken as the study population sample to gather various perspectives by surveying 13 closed-ended questions.
This helps maintain the study’s quality (Dufour and Richard, 2019). The use of this type of data increases the researcher capacity to make informed choices thus improving authenticity and relevance of study. Using quantitative data facilitates the measured evaluation of customer choice as they pick a tourist destination (Sharma, Sharma and Chaudhary 2020).
Social media platforms are measured by conducting surveys and questionnaires to determine the perceptions of travellers and their decisions on searching for Indian travel destinations. By analysing the quantitative data, researchers can determine patterns in social media as they reflect the views and opinions of the 115 survey respondents. This is made possible by the use of a questionnaire with 13 questions, two of them demographic and the remaining twelve are Likert scale.
In this study, the respondents selected are regular users of social media platforms. The study is aimed at the analysis of survey results as a tool for determining decision-making approaches and patterns utilized by social media users in tourism while creating a list of desired places to visit.
The study connects with survey respondents who are active users of social media which enables the identification of pertinent data concerning the issue. They also use quantitative data to make an association between information quality and self-congruity which further help them develop their prior knowledge (Zhang, 2021). SPSS can be possible by applying quantitative data, which helps determine the impact of social mediators and find the correlations among different variables.
For instance, numerical values and percentages can be used by researchers to determine the social media usage frequency and the tendency of users to select a specific travel location in India (Chatterjee and Dsilva, 2021).
Through conducting primary quantitative data collection researchers can provide evidence to the readers so that they can recognize the influence of social media for deciding their tourist destination in India, On the other hand, this type of data is used to maintain the quality of the selected information by reducing the risk of any kind of biases.
SPSS (Statistical Package for Social Sciences) can be used as an effective tool to analyse the primary quantitative data which are collected from 115 participants who frequently use social media platforms. Using Descriptive statistics like median, mode, mean, and standard deviation, and be produced by SPSS. This helps to find out the answers of 13 Likert scale questions
This is used to find accurate and unbiased information to meet the objectives of the study. Frequency analysis as facilitated by SPSS is used to analyse and compare the similarities and differences in responses from survey questions. This method can result in more specific data compared to calculating the frequency with which certain beliefs or prerequisites are associated with the choice of a trip destination. Researchers can use SPSS to determine the relationship between variables, namely vacation places detoxification and frequency of social media usage. This can be used to provide statistical data which provides more accurate data to future researchers and raiders.
In this quantitative study, data was collected by conducting the of 115 participants SPSS used to analyse that data which was used to clarify specific phenomena to generalised data by observing the responses of the diverse participants. The link between an independent variable and a dependent variable can be identified by using SPSS.
The main advantage of using this tool is that it has an easy Graphical User Interface (GUI), making it simple to find better results by analysing the responses of the surveys. It has a comprehensive statistical capability to create variables from preexisting data, which provides a better result.
Observing multiple responses. SPSS used to find numerical values, percentages and statistics to develop the knowledge of the researchers This is used to share enough evidence with future researchers and readers (Sen and Yildirim, 2022). SPSS analysis is used to provide the values and studs through generating tables which are used to find the justification of the research hypothesis.
The study employed the convenience sample strategy since it was a cost- and time-effective method. In contrast to probability sampling, which entails the researcher choosing participants at random, convenience sampling chooses individuals based on their accessibility and availability.
Most often, this approach is selected because it is practical and effective, particularly when random sampling would be challenging or costly to carry out. Convenience sampling, in contrast to probability sampling, does not guarantee known and specified selection probabilities, which could cause bias in the sample.
Chia, Lee, and Han (2020) employed convenience sampling as a means of obtaining a deeper understanding of the distinct viewpoints held by individuals across a range of age groups that utilize social media platforms like Facebook, YouTube, and Instagram. The choice to employ convenience sampling was motivated by the practical benefits of quickly obtaining participants without the requirement for an intricate screening process.
Convenience sampling offers a significant benefit over random sampling in terms of lower costs and easier execution. This sampling technique is usually applied when getting insights from a varied group quickly and efficiently is the main objective. However, selection bias—the possibility that those who are more readily available or ready to participate may not accurately represent the overall population is a serious drawback of convenience sampling.
The 115 participants in this study's sample size were selected to strike a compromise between effectively managing time and costs and obtaining trustworthy results. The researchers made an effort to reduce bias even if convenience sampling may introduce it by choosing a varied group of respondents.
Convenience and efficiency are two benefits of convenience sampling. Researchers can collect data using this strategy without needing specialized skills or substantial resources. However, limitations and biases resulting from convenience sampling must be taken into account when concluding the general population. Notwithstanding these drawbacks, the study seeks to offer significant insights into the viewpoints and outlooks of users of social media across a range of age groups.
Proper ethics have been maintained while conducting this study, The “Data Protection Act” of the UK has been followed while collecting the data. Privacy and confidentiality of data have been maintained to avoid the leakage of data. On the other hand, the name, phone number and email address cannot be mentioned at any stage.
The researcher ensures the privacy and confidentiality of the data collection process by informing the participants before conducting the survey (Sivasubramaniam et al., 2021). The researcher gave the liberty to participants that they have the option to withdraw their participation at any moment before practising in the survey. Before deciding to participate in the survey, participants are informed about the goal of the study, its advantages, and risks.
The researcher has maintained the anonymity of the participants to maintain the privacy of the participants. A text has been given to the participants so that they can be aware of the procedures and the type of questions they will be asked (Sivasubramaniam et al., 2021). This practice is used to maintain transparency while conducting the survey.
They can initial or sign the permission form if they are willing to participate. Keep in mind that when working with particularly vulnerable groups of individuals, this might not be adequate for informed consent. With this, the data collection method has been conducted by following the guides published by the university to maintain academic integrity and honesty.
In this study, one type of data has been used which is primary quantitative data. Guide to the presence of only one type of data certain limitations have been created. Due to the lack of qualitative data, the quality of this study has been affected.
Only one type of data cannot provide accurate and authentic data to address all the queries and questions of the researcher. It can be observed that the utilisation of a primary quantitative data collection strategy cannot prove different varieties of data which can be beneficial to increase the mould of the researchers and readers.
Furthermore, the conclusions drawn from this data have been impacted by the absence of real-time data. quantitative data provides numerical values, statics and qualitative data provides the idea of different concepts. If the research uses a mixed method by using qualitative and quantitative information, then the researcher will bake to recognise the opinion of interview participants.
Along with the survey interview will be the merger of quantitative and qualitative data (Cash et al., 2022). It has been discovered that real-time data contributes to insightful results. However, due to a lack of secondary information researchers cannot find real-time information and trends of social media platforms. In the study survey strategy was used to provide generalised information rather than scientific information.
If the researcher conducts an interview it will help to find specific information used to identify the benefits or drawbacks of social media while making any reveal-related decisions. Inadequate representation of the target population may make it more difficult for the researcher to accomplish its goals. On the other hand, instead of using random sampling techniques, the application of purposive sampling techniques will be beneficial for this study.
Through random sampling, the research selects the participants randomly. If the researcher used purposive sampling, they could find those participants who could help to fulfil the purpose of the study (Savela, 2018). The size of the sample is not sufficient; only 115 participants have been chosen for the survey.
If the research increases the sample size, they can find a variety of data which can reduce the chance of error. A small population cannot help to make the research question meet the aims and objectives. A small sample size creates a location to find more relevant data. In future studies, research needs to increase the size of the sample to make the study more important and relevant.
| Name of tasks | Start date | End date | Duration |
| Introduction | 21-03-23 | 28-03-23 | 7 |
| Aims and objectives | 29-03-23 | 31-03-23 | 2 |
| Research questions | 01-04-23 | 02-04-23 | 1 |
| Literature review | 03-04-23 | 28-04-23 | 25 |
| Research methods | 29-04-23 | 05-05-23 | 6 |
| Data analysis | 06-05-23 | 26-05-23 | 20 |
| Conclusion and recommendation | 27-05-23 | 12-06-23 | 16 |
| Expected outcomes | 13-06-23 | 17-06-23 | 4 |
| Limitations | 18-06-23 | 20-06-23 | 2 |
Table 1: Research Timeline
(Source: Self-developed)
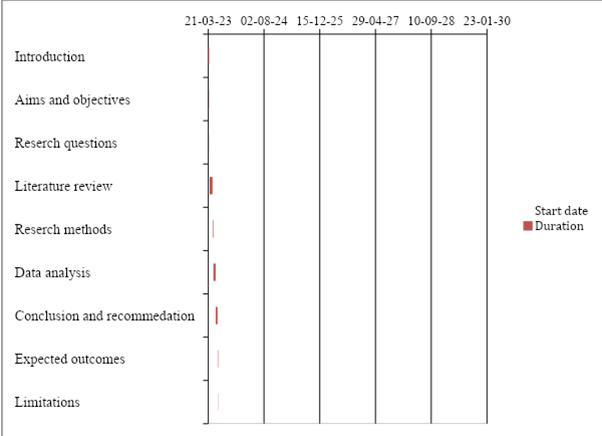
Figure 12: Gantt chart
(Source: Created by the learner)
Observing the overall discussion, it can be summarised that the quantitative research method helps the researcher to analyse the data they collected necessary information from primary sources. The deductive approach, positivism research philosophy and descriptive design are used to find out the positive and negative impact of social media which influences the selection intention of the tourist. Along with that application, SPSS used to analyse the responses of the population.
The result of the survey increases opportunities for the research to provide recommended strategies to the readers so that they can avoid mistakes while choosing their preferred tourist locations. 13 close-ended questions have been asked to the 115 survey participants who are using social media to make effective decisions for deciding tourist locations in India.
Along With this application, the positivism philosophy is used to review and evaluate quantitative information and offers opportunities for the research team to develop their knowledge and insights. Descriptive design and deductive approach both are appropriate for finding better results by interpreting the collected information.
This design and approach are used to develop the resources of primary quantitative research. The timeline guides the researcher to submit the overall study before the deadline to make this study more time effective.
The main objective of exhaustive examination and elucidation of the data acquired during this empirical investigation. India encounters intricate interplay between consumer consciousness and social media platforms when it comes to selecting a major tourism destination. The chapter provides descriptive statistics pertaining to the socioeconomic status, ethnicity, and income of a number of participants, in addition to conducting a sample inquiry into their social media usage. Preliminary testing serves as a foundation for subsequent comprehensive analyses, which may include one-way analyses, regression, crosstabs, and relationships (Schiavenato, M. and Chu, F, 2021).
ANOVA and Factor Analysis can also be utilized as instruments. Diverse inquiries employ distinct analytical techniques, which are not only utilized to examine models and hypotheses in depth but also to identify discrepancies among them. By combining various statistical methods, it is possible to investigate the influence that social media exerts on individuals' travel choices. This facilitates the identification of numerous factors that influence consumer behavior.
The chapter proceeds from quantitative analyses to factor analysis in an effort to identify the fundamental structures of the data. It is beneficial for them to isolate these implicit factors that participants identify with in their perceptions.
However, the comprehensive analysis provided by the ANOVA results reveals areas of disagreement between the groups. A synopsis is provided of the overarching results of the empirical study in order to provide practical recommendations for tourism stakeholders. The narrative seamlessly shifts from rigorous statistical analysis to practical implementation.
The descriptive statistics offer a comprehensive and illuminating examination of individuals' perspectives regarding social media, which serves as a primary means for them to obtain information regarding destinations. This intricate correlation between social media and the tourism industry is examined through a dataset comprising 115 participants and a variety of demographic and behavioral factors. This inquiry establishes a foundation for a comprehensive examination of the ways in which individuals utilize social media platforms in their diverse manifestations to shape their travel decisions.
The analysis commences with an in-depth examination of the gender statistics contained within the dataset. An interesting symmetry exists between them, as males and females are divided equally. However, this gender balance lays the groundwork for a more in-depth examination of the relationship between these discrete social media genders and the acquisition of tourism-related knowledge.
The investigation progresses, and the focus shifts to discerning the nature of the professional status represented by the values. This reveals a complex mosaic of professions, with the arithmetic mean (3.44), which suggests that many professional roles are amalgamated within the surveyed population.
Age, an essential demographic variable, is subsequently examined. It varies between 1 and 5. This indicates that numerous age categories are represented within this range.
Based on the calculated average age of 3.21, the demographic is younger and more technologically literate, suggesting that they are an active group. In addition to introducing an additional dimension, the accompanying standard deviation of 0.941 exposes the extent of variability in the age distribution, thereby highlighting the true heterogeneity of the cohort under study.
This multifaceted perspective on age dynamics serves as a foundation for examining how different social subgroups utilize social media platforms in their pursuit of tourism-related information.
The subsequent factor is time spent on social media networking (Shang et al., 2021). With an average of 3.51 and a standard deviation of 094; therefore, we can conclude that social media is utilized by a significant proportion of the members in some capacity; however, there are variations among users in terms of frequency.
The intricate comprehension of how individuals utilize social media platforms provides a substantial foundation for analyzing the evolving characteristics of their online lives. The application platforms for content related to tourism are subsequently examined, revealing a multifaceted and intricate ecosystem. Participants, with a mean score of 4.05 on a scale of 1 to 6, exhibit a preference for platforms that provide the greatest variety of content.
The standard deviation (1.303) points toward an even wider divergence in the choice of platform, since there are so many different types to begin with. It is clear that this analysis goes further than merely quantitative analyses to provide a qualitative appreciation of things which make people choose these particular media platforms as sources when seeking information about tourism and holidays.
This research doesn't rely only on quantitative indicators but also explores how social media may have impacted individuals 'travel decisions. These statistics, whose standard variation is 1.520 and the mean value reached3.97 clearly indicate that vacationers' choice of holiday destination has been much affected by information distributed on these social media sites about places to visit during their vacations at home as well as abroad.
Adding qualitative factors to the cyber analysis leads us to a fuller understanding of how social media affects people's decision making at different stages in their travels and thus provides greater knowledge.
The research looks at how technology-disadvantaged areas are solving the problems brought on by a lack of technical expertise in specialized social media platforms.
With a mean of 3.4 (SD = 1.408), the judgment outcomes reveal that participants had, in general, not such simple attitudes about this matter as might be taken for granted at first glance. Therefore, channels that focus on a particular brand can indeed bring about tremendous benefits in combating the problems of technical insufficiency; they even raise to an exquisitely refined level.
By making a focused and comprehensive study of descriptive statistics, we can get to the bottom answers about how people search for information on social media websites.
Every statistical metric serves as an entrance to more profound strata, facilitating in-depth examinations through the application of sophisticated statistical techniques (Sharifpour et al., 2018). As the complex fabric of data progressively unravels, it not only sheds light on quantitative aspects such as the extent of participants' engagement but also furnishes a qualitative discourse that delineates decisions pertaining to tourism and unveils a wealth of social media experiences.
By engaging in this comprehensive examination, readers will not only gain an understanding of the current state of social media dynamics but also gain an early advantage over future research endeavors in this era of accelerated change.
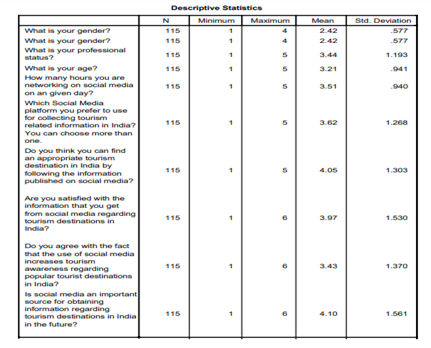
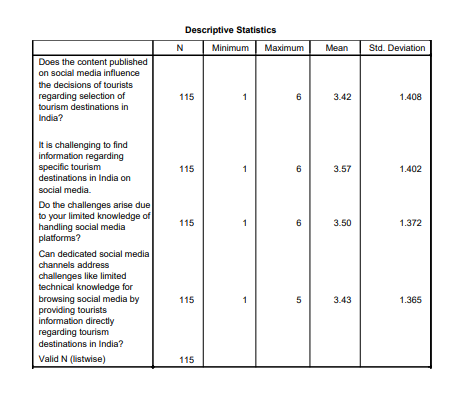

Figure 11 : Challenge arise due to limited knowledge.

Figure 12: Networking on social media age wise
Figure 13: Professional status

Figure 14 : Frequency of challenges like limited technical knowledge

Figure 15: social media platforms
The use of correlation analysis for Hypothesis 1 was based on its appropriateness in evaluating the connection between individuals' competency in utilizing social media platforms and the obstacles encountered in social media and tourism in India. The data shows a substantial positive association (Pearson association = 0.476**) that confirms the hypothesis (Sharma et al., 2020). This indicates that as proficiency improves, issues related to social media and tourism also increase.
The mentioned content seems to pertain to some form of statistical analysis. By employing Pearson's correlation coefficients, we can examine the connections between different factors connected to social media and tourism in India. The analysis presents correlations of coefficients and significance levels for various pairs of variables.
The first group of correlations draws out the challenges resulting from ignorance about using social media platforms. A correlation coefficient of 0.476** between obstacles and inadequate knowledge indicates a moderately high positive link. At a significance level of 0.00, this connection is statistically significant at the 99% confidence level.
Consequently, individuals with little proficiency in managing social media platforms are likely to encounter more challenges. Hence, it is evident that there is a definite correlation between obstacles and the acquisition of expertise in social media.
Further sets of correlations examine the connection between content posted on social media and its impact on tourists' decisions regarding places in India. The correlation coefficient of 0.521 is a moderately positive value that is statistically significant at the 0.01 level (Sig = 0. Et al., 2022)
The analysis also considers the respondents' occupational status as a variable. The correlation coefficient between professional status and issues is 0.146, indicating a positive but weak association. The significance level of 0.119 suggests that there is no statistically significant relationship between the two variables. This indicates a tenuous correlation between one's professional standing and the issues arising from the functioning of social media platforms.
The subsequent set of correlations examines the preferred platforms in India for obtaining information on tourism. The coefficients demonstrate relationships ranging from weak to moderately strong, with values ranging from -0.018 to 0.154. Regrettably, none of these associations exhibit statistical significance, as indicated by all Sig. values over 0.05.
Consequently, there is no discernible correlation between one's professional status and their preference for a specific social media site when it comes to acquiring tourism-related information. Regarding the influence of social media on tourism awareness, there is a strong positive connection (correlation coefficient = 0.521) between the use of social networking and tourism consciousness. This association is statistically significant (Sig. = 0), indicating that as social media usage increases, so does awareness of tourist destinations in India.
In the analysis investigates the potential for social media to emerge as a significant source of tourist information for places in India. The correlation coefficient of 0.309** indicates a moderate positive relationship, which is statistically significant (Sig=5-1). There is a significant correlation between the perceived future significance of social media as a source of information for tourism destinations and its effectiveness in sharing reports about specific topographic units and their corresponding visitor attractions.
Result for Hypothesis 1: The correlation analysis conducted in the content indicates a statistically significant positive association (Pearson Correlation = 0.476**) between individuals' competency in using social media platforms and the issues they encounter in the context of social media and tourism in India. The reported significance level (Sig.) is 0.000, which falls below the customary threshold of 0.05.

Table 2 : Correlation
Regression analysis was selected to investigate the correlation between persons' professional position and their proficiency in overcoming technical challenges when using dedicated social media platforms for tourism information (Singh, S. and Srivastava, P, 2019). This approach enables a thorough analysis of how professional status, as an independent variable, affects the dependent variable.
The regression analysis performed in this study provides a comprehensive and reliable model to solve the various challenges of insufficient technological literacy among operating platforms for tourism information as it is. This issue is viewed as a serious obstacle in the area of technology. Therefore, upon the performance of this research, it sheds light on both issues such as whether the model is appropriate for a given scale and if there are any predictions can really be made in an accurate manner.
Furthermore, the variables that influence the model are broken down into coefficients and sorted out after ANOVA tables as well as residual statistics.
0.907 is a significant R-square value, meaning that there was a high level of explanatory power in this analysis (Sivasubramaniam et al., 2021). 3 This figure depicts the model’s high degree of expertise in illuminating as much as 91% of the changes in the dependent variable.
The dependent variable is covered in this study; it refers to the potential for dedicated social media channels overcoming technical barriers. Adjusted R-square value of 0904 provides further reinforcement to the high efficiency of the model despite the limitations brought by a rather limited sample size and an abundance of predictors. This changes reduce the probability of overfitting and thus the artificial inflating of performance.
In addition, the model's capacity to accurately forecast outcomes within a small margin of error, namely with a standard error of 0.424, enhances its effectiveness in capturing the essence of this social phenomenon.
An examination of the coefficients on an individual basis in this model reveals valuable insights into how each variable either promotes or inhibits expenditure. When examining the constant, which serves as a reference point, it possesses statistical significance and hence does not exert any noticeable impact on the dependent variable.
However, it was found that the professional level of participants is a noteworthy predictor (Beta = 0.34, p < .257), though with a very small impact size. The professional status of an individual appears to have a multifaceted impact on overcoming technical challenges in social media that pertain to obtaining tourism information.
Moreover, the role of social media in promoting tourism is found to have a significant impact on the model (Beta = 0.945, p < 0.01), indicating that it is one of the key nodes with high influence and directional power. The impact of social media on tourism awareness serves as evidence that these platforms are sources of information, but rather potent tools for influencing perceptions and producing visual representations.
Another interesting aspect is the moderately strong influence exerted by widely used social media (Beta = 0.036, p = 0.243). This effect size, while not that great, suggests a relationship between choosing one particular platform and overcoming these technical difficulties on this specific medium. This suggests that there are some platforms which may be better prepared, or more convenient and user-friendly for technical obstacles to users' seeking out information about tourism.
On the other hand, daily time spent on social media is statistically insignificant (beta = 0.08; p-value = .742). This unexpected outcome makes us wonder about the effectiveness of prolonged social media activities in solving technical difficulties. It calls for additional research to see if more time spent on these platforms directly leads to better technical proficiency, or whether other factors take precedence (Sotiriadis, 2017).
The analysis of variance extends beyond the coefficients and offers further evidence supporting the model's overall significance. Statistically speaking, the ANOVA findings are markedly low with a p-value of less than 0. This demonstrates that the predictors have made a joint account of changes in the dependent variable, which strengthens our belief in model validity. The statistically significant ANOVA results show that the proposed model can capture all aspects and nuances in how predictors relate to dependent variables.
Statistics are an essential component that facilitates a model's comprehension of the intricacy of the entity being assessed. The strong correlation between estimated and observed values is evident in the residuals, which are confined to a narrow range of -2.830 to 2.884. The residuals denoted by the observations at approximately 3.43 in Figure 1, are the resultant discrepancies between the predicted and observed values.
The model consequently corresponds reasonably well with the observed data. The presence of these standardized residual statistics, which are expected to have a mean value of 1.00 and no absolute values greater than two or less than one, typically provides evidence for the suitability of the model. For instance, the consistency of residual statistics ensures that these variations in constant values of dependent variables are recorded and represented without exaggeration.
According to the regression model, the correlation between technical proficiency and discernible merits via specialized social media platforms constitutes a negligible portion of a significant phenomenon. An analysis of the relationship between professional rank, opinions regarding social media use and its influence on tourist knowledge and determination to pick learning platforms can give a wider understanding as obstacles in technology are factors that promote the dissemination of travel information.
Result for Hypothesis 2: The regression analysis is considered to be significant, as it has a large explanatory power, low p-value in ANOVA and the residuals are not detectable from an overall pattern Sun et al., 2021. The model effectively reflects the intricacies of poor technical skills in various tourism information systems.

Table 3: Model Summary and ANOVA
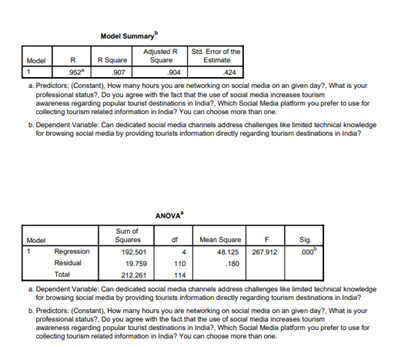
Table 4: Coefficients

Figure 16: social media channels address challenges
The Hypothesis 3 was selected for chi-square analysis because the variables were categorical in nature, such as the participants’ anticipated future participation and current assessments of social media platforms (Tandon et al., 2020). The chi-square test is suitable to evaluate correlations between categorical variables, and thus it can be used for the purpose of the hypothesis testing.
The research’s cross-tabulation gives a deep insight into the connection between social media, its appearance and how the problem of unsatisfactory information in tourism can be solved. The various replies from the participating parties have a potential to broaden the scope of research as they delve into patterns, details and varieties associated with these themes. The initial cross-tabulation serves as a foundation for assessing the efficacy of formal channels in resolving technical issues.
These comparisons aid in comprehending the caliber of the information and also offer data for those who discovered new locations through social media to form distinct impressions about its technical efficacy. This multidisciplinary research is firmly based. The scholar can effortlessly navigate among the multitude of participants' opinions in the jungle. It demonstrates that social media fulfils two purposes: as a platform for obtaining knowledge and solutions to technological issues.
Upon examining an additional cross-tabulation, it has been found that there is a comprehensive dataset containing quantitative analysis and extensive evaluation of this effect across several channels. The trajectory of user preferences is now starting to emerge.
Their impact on the impression of efficacy is significant. This extensive range of reporting allows us to thoroughly examine the intricate connection between user preferences, selection of social media platform, and perceptions regarding technical obstacles (Tang, M. and Liao, H, 2021). At this level of study, it becomes evident that users communicate with social media platforms in many manners, and there exists a dynamic interplay between the characteristics of the platform and the expectations of the users.
The final cross-tabulation offers a comprehensive examination of the association between participants’ time spent on social media networking and their confidence in the ability of social media channels to effectively address technical issues. This study thoroughly examines the correlation between social media involvement and the comprehension of utilizing these technologies by incorporating the comments of all participants. Analyzing the relationship between the amount of time spent and the level of technical convenience provides a more comprehensive insight into the nature of social media.
The fourth cross-tabulation explores the connection between participants' expected future involvement in supplying tourism information through social media and their current assessment of each channel's ability to address technical issues. Due to the quantity of responses in this dataset, we will have the opportunity to thoroughly investigate the intricate relationship between future expectations and the present opinions expressed by social media participants.
By adopting a forward-thinking approach, one may extract numerous significant information regarding the evolving importance of social media in the tourism industry. Additionally, it allows us to anticipate how future developments may impact current perceptions of technological efficiency.
The last cross-tabulation examines the association between the frequency with which participants perceive posted stickers on social media to affect visitors' decisions and their belief in a platform's ability to effectively resolve technical issues, with precise accuracy. This research analyses the strong correlation between the impact of content and technical professionalism by considering the entire group of participants.
This research provides a comprehensive conceptual framework for understanding how visual features impact decision-making and problem-solving processes in a technical environment. The combination of these cross-tabulations produces a graphic, which in turn allows for the construction of an overall analysis of the intricate relationship that exists between social media and tourism information.
Through the analysis of this enormous dataset, which has such a high level of reliability for identifying observable patterns, we are able to get a significant understanding of the deep relationships that exist between all of these active components in a world that is constantly evolving.
When it comes to the complex interaction between levels and forms of social media engagement, differences in preferences regarding platforms, and temporal concerns about when content will spread visually the most following it has been organized by own for each cross-tabulation serves as the lens that provides us with different perspectives on the research that we conduct (Tham et al., 2019).
Thus, such a comprehensive analysis of the intricacies not only increases our knowledge about the rituals associated with social media. Moreover, not only does it provide a foundation for further research but also helps scholars, market players and public managers delve into uncharted waters as they venture into the world of available tourism information.
Result for Hypothesis 3: The various interpretations provided by these same analyses help understanding while they also provide a robust basis for further research, enabling researchers, market players and public officials to navigate emerging fields in the accessibility of tourism information.
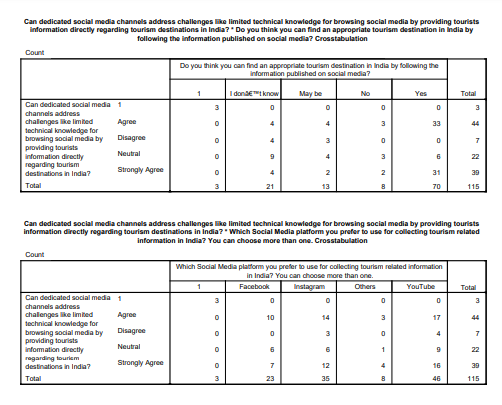
Table 5: Chi-Square-1 and 2

Table 6: Chi-Square-3
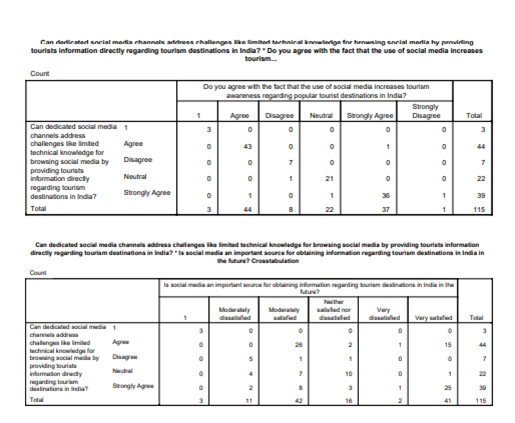
Table 7: Chi-Square 4 and 5
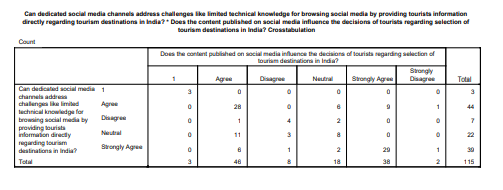
Table 8: Chi-Square-6
The degrees of freedom in the model 114 participants provide a full evaluation of dispersion. 2.710 F-statistic with 0.034 significance threshold is important while analyzing the answers provided by different participants. The estimated F-statistic is greater than the critical value of 6.3, meaning that there are significant differences in perceptions about the effectiveness among the mentioned categories.
ANOVA analysis reflects a compelling viewpoint concerning the various opinions by participants evaluating the potential for a specialized social media platform to fill in gaps of technical information Thirumaran et al., 2021. First, the F-statistic is a very important indicator, which shows that it might be necessary to perform an in-depth analysis of hidden features.
Uncovering these intricacies may help us understand more about the myriad points of view within this group and provide a sophisticated description of how various societies judge the effectiveness of social media platforms aimed at solving technical issues. After scrutinizing the numerous categories of statistical findings, it is evident that ANOVA outcomes only measure differences in individuals’ responses.
The targeted group includes various points of view concerning several features, such as their professional position, opinions on the impact social media has on tourism awareness and attitudes towards different platforms. The ANOVA facilitates a look into various phenomena linked to social media and tourist information. Moreover, it suggests an opportunity to increase our awareness of what makes users see specialized social media platforms as extremely valuable and next to data analysis (Țuclea et al., 2020).
Statistical arguments are inextricably linked with the complex and intricate web of human experiences, perspectives, and outcomes. Their use of social media is changing.
In this way, common people are reshaping the perception of these platforms not only an information consuming tools but also a system that work based on supply and demand for knowledge.
Result for Hypothesis 4: ANOVA analysis gives a reliable and statistically significant picture of how specific social media platforms are effective. The study’s findings imply that people’s view of efficacy depends on categories, meaning it is essential to know how what factors result in these differences.
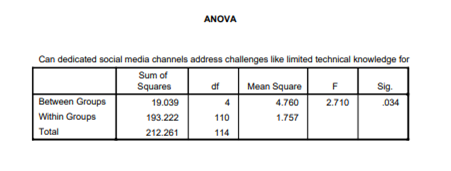
Table 9: ANOVA
Factor Analysis is an acceptable method to study the relationships between various items obtained from PCA and their connections with tourism-related variables. It is thus an appropriate test for Hypothesis 5. Factor Analysis is a statistical method that helps to identify latent elements and their effect on observable variables.
Research about PCA helps achieve a full understanding of the relationships between root connections and shared variation among variables. This helps gain a comprehensive understanding of the different elements that affect social media in the intricate field of tourist information. Communalities form useful indices representing the amount of variability in each variable that is accounted for by the collected components.
They provide a comprehensive explanation of the significant and extended contributions made by each aspect to this research. Communalities in PCA are quantitative metrics that indicate the amount of variability in the original variables that is accounted for by each recognized component. The communalities vary between 0.053 and 1.
The degree of correspondence between the components and the identified changes on various survey questions is of utmost importance in these calculations. The variable that is meant to indicate the amount of time spent on social networking each day has a rather low communality of 0.053. This indicates that an important amount of its variability is still not accounted for by the factors identified in the study, implying the existence of a possible knowledge gap that requires additional investigation.
Exploring the complex domain of factor analysis, each eigenvalue serves as a guiding light, revealing the importance of a specific extracted component. The first component, with an eigenvalue of 2.936, explains a significant 41.948% of the total variation on its own. The second component, possessing an eigenvalue of 1.250, contributes an extra 17.862%, together accounting for 59.810% of the variability in the dataset. These two components play a crucial role in summarizing the intrinsic complexity of the dataset.
One of the most important aspects of factor analysis is the component matrix, which investigates the link between the variables that were initially used and the components that were recovered. In response to the difficulties associated with gaining access to specialized tourism information on social media platforms, Component 1 was developed as a targeted response (Wang, H. and Yan, J, 2022).
The objective is to address the gap created by those who see social media as a source of knowledge and to overcome challenges related to inadequate technological skills. Component 2 may be assessed based on variables such as individuals' preference for the information they get on social media, as well as the duration of their engagement in activities in coffee shops and bars.
Furthermore, they are confident that their quest for high-quality trips through the Internet has yielded profitable results. The loadings in the component matrix show how strong and in what direction a given variable is correlated with its corresponding components. For instance, the variable that represents the time spent on social media networking has comparatively weaker links with both components indicated by its factor loadings. It is the use of this advanced analysis of connections that makes us understand better what mechanisms work inside the dataset (Wang et al., 2019).
As an analytical method, factor analysis shows that most participants’ answers fall in separate components. These components greatly impact, especially in explaining more than fifty percent of the variance of a specific survey variable. The results provide further information regarding the interconnectedness of these components, hence defining five critical structures that come within the original information. Analysis of these components provides a more accurate perception of the correlation between different aspects of social media perspectives and tourism information.
Result for Hypothesis 5: The Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and Factor Analysis offer useful insights into the significance and connections among many factors when examining participants' viewpoints on social media and tourism information.
Table 10: Total Variance Explained
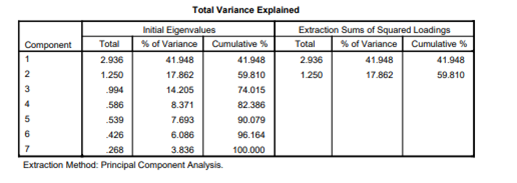
Table 11 : Communalities

Table 12: Component Matrix
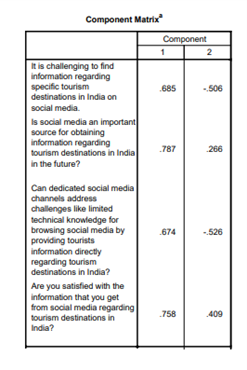
The main contribution of the study specifies relationships between social media and tourism information from the point of view of India. There is a clear and strong correlation between people’s level of proficiency in using social media technologies and their challenges within the framework of social media, tourism. This underlines the significance of having appropriate technical skills to navigate social media platforms for use in tourism information search.
The regression research emphasizes how professional position influences people’s ability to deal with technical barriers influencing their use of specialized social media platforms in obtaining tourism information. This sheds light on how an individual’s work experience impacts higher ability to manage technical issues in the intersection of social media and tourism.
Cross-tabulations show convincing evidence in support of the correlation between participants anticipated future contributions related to sharing tourism information through social media and their current perception about each channel’s ability for technical troubleshooting. Apparently, people’s ideas about how well social media would be able to handle technical issues in the tourism industry are strongly associated with their future aspirations (Werenowska, A. and Rzepka, M, 2022).
The results of ANOVA analysis show that specialized social media platforms play an important role, vacillating between observable insights in relation to the level of technical competence among participants. This emphasizes the need for tailor-made approaches that consider different user segments based on their technical proficiency levels.
Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and Factor Analysis offer a detailed description of the extracted components to understand fully how social media opinions are related with tourism information factors. These findings can allow for a more profound understanding of the complex connection between social media and tourism information. They have both academic and practical relevance in the travel industry.
This study provides a detailed analysis of the mutually beneficial relationship between social media and tourism information in the case of India. Including the findings is a major aspect of significance because it shows that an individual’s ability to effectively use social media platforms demonstrates a remarkable correlation with challenges arising within tourism and information technology.
This highlights the importance of providing dedicated interventions to address this disparity in technical competence among users and the research indicates a strong correlation between individuals’ professional level and their ability to overcome technical obstacles while using certain SMPs for obtaining tourism relevant information.
In order to develop strategies that address the needs of various user groups, it is crucial to recognize how professional backgrounds impact technical expertise. The cross tabulations show the correlation between participants’ willingness to continue offering tourism information through social media in future and their current assessment of how well each channel copes with technical issues. Such findings are essential for understanding how user’s expectations and involvement with social media in terms of travel information keep changing.
The ANOVA analysis indicates that participants of various levels of technical proficiency may perceive the capabilities and interfaces on specialist social media platforms differently. There would be a requirement to implement special strategies that enhance user experience, depending on the distributed nature of technical skills among users. PCA and Factor Analysis provide a more profound understanding of the factors that influence social media views as well as their relationship to tourism information-related variables (Wibowo et al., 2020).
This offers a great platform to understand how social media influence’s opinion and choices regarding tourism are very complicated. These results have significant implications for industry as they provide a valuable understanding of different aspects essential to the development of social media platforms being utilized by people in their search for quality, reliable information about travel destinations.
The implications of this research can be seen as multiple and substantial both for studying tourism and social media, but also from a practical standpoint on how to utilize findings presented. The positive correlation between peoples’ ability to use social media platforms effectively and the problems faced in the world of digital interaction with tourism points towards an important need for initiatives on getting people digitally literate.
Education programs that bring about the enhancement of users’ technical competence can help make it easy to introduce social media into tourism information space. Moreover, the correlation between professional status and technical competence underlines the need for tailored solutions targeting specific groups of professions. Recognizing that people with different professional backgrounds are likely to have distinct levels of proficiency when it comes to dealing with technical challenges, proper custom-made assistance and user interfaces need be offered that reflect users’ respective specific occupational context.
The results related to the future interest of users in sharing information about tourism via social media and their present assessment of possibilities on handling technical issues reflect increasing user requirements. Therefore, tourism-related companies and platforms need to be ready for changing user behaviors while ensuring that aspects of technology are in sync with how consumers will most likely interact in the future.
From the results of an ANOVA analysis, it is found that users perceptions regarding specialized social media platforms vary based on their technical expertise. By identifying these differences, designers of platforms and the tourism companies can help customize their offers to suit different user groups which would increase customer satisfaction as well as participation.
The Principal Component Analysis Factor Analysis offers useful insight into the staying of social media strategies in tourism commerce (Wong, 2023). A thorough understanding of the core principles influencing social media perceptions can be used as a guide to be designing content, creating platforms, or even planning out user engagement strategies. This will lead to better coordination between social media and the various components that influence tourism information.
The different recommendations come out as improving collaboration among social media and tourism information in India and there is an evident need for consumer-focused digital literacy initiatives that enhance their competence in managing social media platforms. These activities should cover a very broad spectrum of groups and be customized to reflect varying degrees of technological competence. Travel companies and social media platforms should develop personalized solutions that consider the influence of professional position on technical knowledge.
Bespoke help and interfaces tailored to different professional areas will ensure a more intuitive, easily accessible user experience. It is also important to predict how people will contribute to the future by offering tourism information via social media. Businesses need to proactively change their technology features in concert with changing user expectations, ensuring continued usefulness and participation.
The designers of platforms and companies involved in tourism must take into account that specialized social media platforms may have different interpretations by users with various levels of technical proficiency. Interactive features and content are modified to accommodate different user groups, enhancing satisfaction levels and efficiency. It is necessary for content developers and designers of social media platforms to focus on the critical aspects that influence people’s views about social media as a whole based on what Principal Component Analysis showed us or Factor analysis. While aligning this strategy can optimize the general effectiveness of social media in impacting tourism impressions and choices.
Future studies in the field of social media and tourism within India can focus on exploring new technologies that are just emerging now, as well. Investigating how augmented reality AR or virtual reality VR could be incorporated into social media platforms would also provide helpful insights in terms of their effectiveness to enhance the level of participation and decision-making among tourists and investigating the role of new social media platforms or functionalities like audio-based social networking, live streaming in shaping attitudes to tourism offers a stimulating prospect for future studies (Wright et al., 2021).
It would help us understand how these changing platforms impact on travel decisions and the spread of information as we strive to learn more about an ever-changing environment. The long-term projects carrying out observation of the evolving patterns in social media use for travel purposes could offer a temporal dimension to research. Studying the changes in user behaviors, preferences and issues on a long-term basis would assist enterprises.
It would be appropriate to discuss the potential impact of off-site factors such as global happenings, economic oscillations or health issues in public on the role that social media can play for tourism. For stakeholders, a sharp evaluation of the resilience and adaptability of social media as an instrument for disseminating tourism information under conditions that are unpredictable could well provide strategic insights. Future studies can look into technologies being developed, evolving ideologies of platforms for greater understanding on variance and how suspension between social media and tourism will always remain dynamic in the Indian scenario.
Abutabenjeh, S. and Jaradat, R., 2018. Clarification of Research Design, Research Methods, and Research Methodology. Teaching Public Administration, 36(3), pp.237–258.
Adgully, 2022.YouTube's most-used social media platform by influencers in India - Adgully. Available at https://www.google.com/url?sa=i&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.adgully.com%2Fyoutube-most-used-social-media-platform-by-in-uencers-in-india-112149.html&psig=AOvVaw07tQxRi3rqVbD0kltWHq01&ust=1685623588793000&source=images&cd=vfe&ved=0CBMQjhxqFwoTCOCSlPDMn_8CFQAAAAAdAAAAABAJ
Aftab, S. and Khan, M.M., 2019. Role of social media in promoting tourism in Pakistan. Journal of Social Sciences and Humanities, 58(1), pp.101-113.
Agyapong, E. and Yuan, J., 2022. Social Media Impact on Tourism Destination Decision: Evidence from International Students in China. Open Journal of Applied Sciences, 12(12), pp.2055–2080.
Ahmad, R., Nawaz, M.R., Ishaq, M.I., Khan, M.M. and Ashraf, H.A., 2023. Social exchange theory: Systematic review and future directions. Frontiers in Psychology, 13(2).
Al-Razgan, M., Alrowily, A., Al-Matham, R.N., Alghamdi, K.M., Shaabi, M. and Alssum, L., 2021. Using diffusion of innovation theory and sentiment analysis to analyze attitudes toward driving adoption by Saudi women. Technology in Society, 65, p.101558.
Álvarez-García, J., Durán-Sánchez, A. and del Río-Rama, M., 2018. Scientific Coverage in Community-Based Tourism: Sustainable Tourism and Strategy for Social Development. Sustainability, 10(4), p.1158.
Araceli Galiano Coronil, Sofía Blanco-Moreno, Luis Bayardo Tobar-Pesántez and Guillermo Antonio Gutiérrez-Montoya., 2023. Social media impact of tourism managers: a decision tree approach in happiness, social marketing, and sustainability. Journal of Management Development, 42(6), pp.436–457.
Armutcu, B., Tan, A., Amponsah, M., Parida, S. and Ramkissoon, H., 2023. Tourist behavior: The role of digital marketing and social media. Acta Psychologica, 240, p.104025.
Basuroy, T., 2022. Topic: Social Media Usage in India. Available at: https://www.statista.com/topics/5113/social-media-usage-in-india/#topicOverview [Accessed 31 Oct. 2023].
Cash, P., Isaksson, O., Maier, A. and Summers, J., (2022). Sampling in design research: Eight key considerations. Design Studies, 78, p.101077..
Cash, P., Isaksson, O., Maier, A. and Summers, J., (2022). Sampling in design research: Eight key considerations. Design Studies, 78, p.101077.
CFI, 2022. Diffusion of Innovation. Available at: https://corporatefinanceinstitute.com/resources/economics/diffusion-of-innovation/ [Accessed 13 Oct. 2023].
Chatterjee, J. and Dsilva, N.R., 2021. A study on the role of social media in promoting sustainable tourism in the states of Assam and Odisha. Tourism Critiques: Practice and Theory.
Chia, J., Lee, J. and Han, H., 2020. How Does the Location of Transfer Affect Travellers and Their Choice of Travel Mode?—A Smart Spatial Analysis Approach. Sensors, 20(16), p.4418.
Dey, S. and Das, A., 2019. Robotic process automation: assessment of the technology for transformation of business processes. International Journal of Business Process Integration and Management, 9(3), pp.220-230.
Dufour, I.F. and Richard, M.-C., 2019. Theorizing from secondary qualitative data: A comparison of two data analysis methods. Cogent Education, 6(1).
Elfil, M. and Negida, A., 201). Sampling methods in clinical research; an educational review. Emergency (Tehran, Iran), 5(1).
Faber, R., Merkies, R., Damen, W., Oirbans, L., Massa, D., Kroesen, M. and Molin, E., 2021. The role of travel-related reasons for location choice in residential self-selection. Travel Behaviour and Society, 25, pp.120–132.
Femenia-Serra, F. and Gretzel, U., 2020. Influencer marketing for tourism destinations: Lessons from a mature destination. In Information and Communication Technologies in Tourism 2020: Proceedings of the International Conference in Surrey, United Kingdom, January 08–10, 2020 (pp. 65-78). Springer International Publishing.
Govindarajo, N.S. and Khen, M.H.S., 2020. Effect of service quality on visitor satisfaction, destination image, and destination loyalty–practical, theoretical and policy implications to avitourism. International Journal of Culture, Tourism and Hospitality Research, 14(1), pp.83-101.
Gupta , S., 2022. Nearly 1 in 3 Indians middle class, to double in 25 years: Report - Times of India. Available at: https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/business/india-business/middle-class-nearly-1/3rd-of-indias-population-to-be-2/3rds-by-2047-report/articleshow/95239621.cms [Accessed 31 Oct. 2023].
Gupta, S., Manohar Sajnani and Gowreesunkar, V., 2023. Impact of Social Media Platforms on Tourist’s Perception for the Selection of Food Outlets: A Case of Delhi NCR (India). International Journal of Professional Business Review, 8(7), pp.e02568–e02568.
Gupta, V., 2019. The influencing role of social media in the consumer’s hotel decision-making process. Worldwide Hospitality and Tourism Themes, 11(4), pp.378-391.
Hanaysha, J.R. (2022). Impact of social media marketing features on consumer’s purchase decision in the fast-food industry: Brand trust as a mediator. International Journal of Information Management Data Insights, 2(2), p.100102.
Hartanto, Y., Firmansyah, M.A. and Adhrianti, L., 2022, April. Implementation of Digital Marketing Pesona 88 Curup to Build Image for the Decision of Visit Tourist Attraction. In 4th Social and Humanities Research Symposium (SoRes 2021) (pp. 589-594). Atlantis Press.
Hindustan Times, 2021. Maharashtra Govt. introduces policies to promote innovative tourism experiences. Available at: https://www.hindustantimes.com/brand-stories/maharashtra-govt-introduces-policies-to-promote-innovative-tourism-experiences-101635314871641.html [Accessed 13 Oct. 2023].
Huerta-Álvarez, R., Cambra-Fierro, J.J. and Fuentes-Blasco, M., 2020. The interplay between social media communication, brand equity and brand engagement in tourist destinations: An analysis in an emerging economy. Journal of Destination Marketing & Management, 16, p.100413.
Idbenssi, S., Safaa, L., Perkumienė, D. and Škėma, M., 2023. Exploring the Relationship between Social Media and Tourist Experiences: A Bibliometric Overview. Social Sciences, 12(8), p.444.
Imran, F., Shahzad, K., Butt, A. and Kantola, J., 2021. Digital transformation of industrial organizations: Toward an integrated framework. Journal of change management, 21(4), pp.451-479.
Jamil, K., Dunnan, L., Gul, R.F., Shehzad, M.U., Gillani, S.H.M. and Awan, F.H., 2022. Role of Social Media Marketing Activities in Influencing Customer Intentions: a Perspective of a New Emerging Era. Frontiers in Psychology, 12(1), pp.1–12.
Jamil, K., Dunnan, L., Gul, R.F., Shehzad, M.U., Gillani, S.H.M. and Awan, F.H., 2022. Role of Social Media Marketing Activities in Influencing Customer Intentions: a Perspective of a New Emerging Era. Frontiers in Psychology, 12(1), pp.1–12.
Jangra, Dr.R., Kaushik, Prof.S.P. and Saini, Dr.S.S., 2021. An analysis of tourist’s perceptions toward tourism development: Study of cold desert destination, India. Geography and Sustainability, 2(1), pp.48–58.
Joo, Y., Seok, H. and Nam, Y., 2020. The Moderating Effect of Social Media Use on Sustainable Rural Tourism: A Theory of Planned Behavior Model. Sustainability, 12(10), p.4095.
Kar, A.K., Kumar, S. and Ilavarasan, P.V., 2021. Modelling the service experience encounters using user-generated content: A text mining approach. Global Journal of Flexible Systems Management, 22(4), pp.267-288.
Khadka, S. and Khadka, A.K., 2023. The Role of Social Media in Determining Tourists’ Choices of Nepalese Destinations. Journal of logistics, informatics and service science, 10(3).
Kim, S.M., 2021. Inductive or deductive? Research by maxillofacial surgeons. Journal of the Korean Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons, 47(3).
Kumar, P., Mishra, J.M. and Rao, Y.V., 2022. Analysing tourism destination promotion through Facebook by Destination Marketing Organizations of India. Current Issues in Tourism, 25(9), pp.1416-1431.
Kumar, S., Kar, A.K. and Ilavarasan, P.V., 2021. Applications of text mining in services management: A systematic literature review. International Journal of Information Management Data Insights, 1(1), p.100008.
Larasetiati, M. and Ali, H., 2019. Model of consumer trust: analysis of perceived usefulness and security toward repurchase intention in an online travel agent. Saudi Journal of Economics and Finance, 3(8), pp.350-357.
Liu, X., Mehraliyev, F., Liu, C. and Schuckert, M., 2020. The roles of social media in tourists’ choices of travel components. Tourist Studies, 20(1), p.146879761987310.
Liu, X., Mehraliyev, F., Liu, C. and Schuckert, M., 2020. The roles of social media in tourists’ choices of travel components. Tourist studies, 20(1), pp.27-48.
Long, H.A., French, D.P. and Brooks, J.M., 2020. Optimising the Value of the Critical Appraisal Skills Programme (CASP) Tool for Quality Appraisal in Qualitative Evidence Synthesis. Research Methods in Medicine & Health Sciences, 1(1), pp.31–42.
Longdom, 2022.Effect of Social Media on Tourism (Case in Cambodia). Available at https://www.longdom.org/articles-images/tourism-hospitality-creation-9-424-g001.
Luo, J., Dey, B.L., Yalkin, C., Sivarajah, U., Punjaisri, K., Huang, Y.A. and Yen, D.A., 2020. Millennial Chinese consumers' perceived destination brand value. Journal of Business Research, 116, pp.655-665.
Mosley, A.J. and Biernat, M., 2020. The new identity theft: Perceptions of cultural appropriation in intergroup contexts. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 121(2).
Mosley, A.J. and Biernat, M., 2020. The new identity theft: Perceptions of cultural appropriation in intergroup contexts. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 121(2).
Obembe, D., Kolade, O., Obembe, F., Owoseni, A. and Mafimisebi, O., 2021. Covid-19 and the tourism industry: An early stage sentiment analysis of the impact of social media and stakeholder communication. International Journal of Information Management Data Insights, 1(2), p.100040.
Obembe, D., Kolade, O., Obembe, F., Owoseni, A. and Mafimisebi, O., 2021. Covid-19 and the tourism industry: An early stage sentiment analysis of the impact of social media and stakeholder communication. International Journal of Information Management Data Insights, 1(2), p.100040.
Okagbue, H.I., Oguntunde, P.E., Obasi, E.C.M. and Akhmetshin, E.M., 2021. Trends and usage pattern of SPSS and Minitab Software in Scientific research. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1734, p.012017.
Pop, R.-A., Săplăcan, Z., Dabija, D.-C. and Alt, M.-A., 2021. The impact of social media influencers on travel decisions: the role of trust in consumer decision journey. Current Issues in Tourism, 25(5), pp.823–843.
Qureshi, M.H., 2022. Cultural Diversity in India. Journal of Development Policy and Practice, 8(1), pp.13–23.
Rather, R.A., 2021. Monitoring the impacts of tourism-based social media, risk perception and fear on tourist’s attitude and revisiting behaviour in th
Ravindran, D., Nagamalar, M. and Rani, P.U., 2018. Social media sources (SMS) influence on tourism choice decisions. Eurasian Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 13(6b), pp.177-182.
Roy, G., Datta, B., Mukherjee, S. and Basu, R., 2021. Effect of eWOM stimuli and eWOM response on perceived service quality and online recommendation. Tourism Recreation Research, 46(4), pp.457-472.
Saini, H.K., Kumar, P. and Oberoi, S., 2023. Welcome to the destination! Social media influencers as a cogent determinant of travel decision: A systematic literature review and conceptual framework. Cogent Social Sciences, 9(1).
Santi, I.N. and Fadjar, A., 2020. The Function of Social Media as a Promotion Tool for Tourism Destinations.
Saqib, N., 2019. A positioning strategy for a tourist destination, based on analysis of customers’ perceptions and satisfactions: A case of Kashmir, India. Journal of Tourism Analysis: Revista de Análisis Turístico, 26(2), pp.131-151.
Savela, T., 2018. The Advantages and Disadvantages of Quantitative Methods in Schoolscape Research. Linguistics and Education, 44(1), pp.31–44. Sen, S. and Yildirim, I. (2022). A Tutorial on How to Conduct Meta-Analysis with IBM SPSS Statistics. Psych, 4(4), pp.640–667.
Schiavenato, M. and Chu, F., 2021. PICO: What it is and what it is not. Nurse Education in Practice, 56(1).
Shang, Y., Mehmood, K., Iftikhar, Y., Aziz, A., Tao, X. and Shi, L., 2021. Energizing Intention to Visit Rural Destinations: How Social Media Disposition and Social Media Use Boost Tourism Through Information Publicity. Frontiers in Psychology, 12.
Sharifpour, M., Walters, G., Ritchie, B.W. and Winter, C., 2018. Investigating the Role of Prior Knowledge in Tourist Decision Making. Journal of Travel Research, 53(3), pp.307–322.
Sharma, A., Sharma, S. and Chaudhary, M.,2020. Are small travel agencies ready for digital marketing? Views of travel agency managers. Tourism Management, 79(1), p.104078.
Silaban, P.H., Chen, W.-K., Nababan, T.S., Eunike, I.J. and Silalahi, A.D.K., 2022. How Travel Vlogs on YouTube Influence Consumer Behavior: A Use and Gratification Perspective and Customer Engagement. Human Behavior and Emerging Technologies, 2022, p.e4432977.
Singh, S. and Srivastava, P., 2019. Social media for outbound leisure travel: a framework based on technology acceptance model (TAM). Journal of Tourism Futures, 5(1), pp.43-61.
Sivasubramaniam, S., Dlabolová, D.H., Kralikova, V. and Khan, Z.R., 2021. Assisting You to Advance with Ethics in research: an Introduction to Ethical Governance and Application Procedures. International Journal for Educational Integrity, 17(1), pp.1–18.
Sotiriadis, M.D., 2017. Sharing tourism experiences in social media: A literature review and a set of suggested business strategies. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management, 29(1), pp.179-225.
Sun, W., Tang, S. and Liu, F., 2021. Examining perceived and projected destination image: A social media content analysis. Sustainability, 13(6), p.3354.
Tandon, U., Ertz, M. and Bansal, H., 2020. Social vacation: Proposition of a model to understand tourists’ usage of social media for travel planning. Technology in Society, 63, p.101438.
Tang, M. and Liao, H., 2021. From conventional group decision-making to large-scale group decision-making: What are the challenges and how to meet them in the big data era? A state-of-the-art survey. Omega, 100, p.102141.
Tham, A., Mair, J. and Croy, G., 2019. Social media influence on tourists' destination choice: the importance of context. Tourism Recreation Research, 45(2), pp.1–15.
The Economic Times, 2023. How the middle class will play the hero in India's rise as a world power. Available at: https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/economy/indicators/how-the-middle-class-will-play-the-hero-in-indias-rise-as-world-power/articleshow/101608682.cms?from=mdr.[Accessed 13 Oct. 2023].
Thirumaran, K., Jang, H., Pourabedin, Z. and Wood, J., 2021. The Role of Social Media in the Luxury Tourism Business: A Research Review and Trajectory Assessment. Sustainability, 13(3), p.1216.
Țuclea, C.-E., Vrânceanu, D.-M. and Năstase, C.-E., 2020. The Role of Social Media in Health Safety Evaluation of a Tourism Destination throughout the Travel Planning Process. Sustainability, 12(16), p.6661.
Wang, H. and Yan, J., 2022. Effects of social media tourism information quality on destination travel intention: Mediation effect of self-congruity and trust. Frontiers in Psychology, 13.
Wang, W., Ying, S., Lyu, J. and Qi, X., 2019. Perceived image study with online data from social media: the case of boutique hotels in China. Industrial management & data systems, 119(5), pp.950-967.
Werenowska, A. and Rzepka, M., 2020. The Role of Social Media in Generation Y Travel Decision-Making Process (Case Study in Poland). Information, 11(8), p.396.
Wibowo, A., Chen, S.C., Wiangin, U., Ma, Y. and Ruangkanjanases, A., 2020. Customer behavior as an outcome of social media marketing: The role of social media marketing activity and customer experience. Sustainability, 13(1), p.189.
Wong, B., 2023. Top Social Media Statistics And Trends Of 2023. [online] Available at: https://www.forbes.com/advisor/in/business/social-media-statistics/#:~:text=Active%20Social%20Media%20Penetration%20in [Accessed 13 Oct. 2023].
Wright, C., 2021. Social Media Marketing 2020: Cutting-Edge Strategies to Grow Your Brand, Reach Millions of Customers, and Become an Expert Influencer with Facebook, Twitter, YouTube, and Instagram (Vol. 165). Alakai Publishing LLC.
Yadav, M.L. and Roychoudhury, B., 2019. Effect of trip mode on opinion about hotel aspects: A social media analysis approach. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 80, pp.155-165.Yuan, Y., Chan, C.-S., Eichelberger, S., Ma, H. and Pikkemaat, B., 2022. The effect of social media on the travel planning process by Chinese tourists: the way forward to tourism futures. Journal of Tourism Futures.
Zak, S. and Hasprova, M., 2020. The role of influencers in the consumer decision-making process. In SHS web of conferences (Vol. 74, p. 03014). EDP Sciences.
Zhang, Y., 2021. Book Review: Data Collection Research Methods in Applied Linguistics. Frontiers in Psychology, 12.
Zoller, Y.J. and Muldoon, J., 2019. Illuminating the principles of social exchange theory with Hawthorne studies. Journal of Management History, 25(1), pp.47–66.
Žukauskas, P., Vveinhardt, J. and Andriukaitienė, R., 2018. Philosophy and paradigm of scientific research. Management Culture and Corporate Social Responsibility, 1(1).
Appendix 1: Survey Questions
Q1: What is your gender?
(a) Male
(b) Female
(c) Others
Q2: How many hours you are active on Social media?
(a) 1- 2 hours
(b) 2-4 hours
(c) 3-5 hours
(d) 5-7 hours
Q3: Which platform you prefer to use for collecting tourist related information?
(a) Facebook
(b) YouTube
(c) Instagram
(d) Others
Q4: What is your age?
(a) 18 to 25
(b) 26-35
(c) 36-45
(d) 46-55
Q5: Do you agree that social media platforms can help to find tourism destinations?
(a) Yes
(b) No
(c) I don’t know
(d) May be
Q6: Are you satisfied with the information that you get from social media regarding tourism destinations?
(a) Very satisfied
(b) Moderately satisfied.
(c) Neither satisfied nor dissatisfied
(d) Moderately dissatisfied
(e) Very dissatisfied
Q7: Are you able to find an appropriate tourism destination by following the information published on social media
(a) Yes
(b) No
(c) I don’t know
(d) May be
Q8: Are you satisfied with the application of social media to make a better decision while selecting any tourism destination?
(a) Very satisfied
(b) Moderately satisfied.
(c) Neither satisfied nor dissatisfied
(d) Moderately dissatisfied
(e) Very dissatisfied
Q9: Do you agree with the fact that the use of social media increases tourism awareness?
(a) Strongly Agree
(b) Agree
(c) Neutral
(d) Disagree
(e) Strongly Disagree
Q10: Do you think that social is will help in the future to enhance the decision-making practice of Indian tourists?
(a) Strongly Agree
(b) Agree
(c) Neutral
(d) Disagree
(e) Strongly Disagree
Q11: Do you agree that social media can provide sufficient information regarding any tourism destination?
(a) Very satisfied
(b) Moderately satisfied.
(c) Neither satisfied nor dissatisfied
(d) Moderately dissatisfied
(e) Very dissatisfied
Q12: Do you agree with the fact that the content published on social media can influence the decisions of tourists?
(a) Strongly Agree
(b) Agree
(c) Neutral
(d) Disagree
(e) Strongly Disagree
Are you confident that you will achieve the grade? Our best Expert will help you improve your grade
Order Now