$20 Bonus + 25% OFF CLAIM OFFER
Place Your Order With Us Today And Go Stress-Free
HLTAAP001-RECOGNISE HEALTHY BODY SYSTEMS
Name each system below
Fill in the blank rectangle spaces by naming the indicated part in each system.
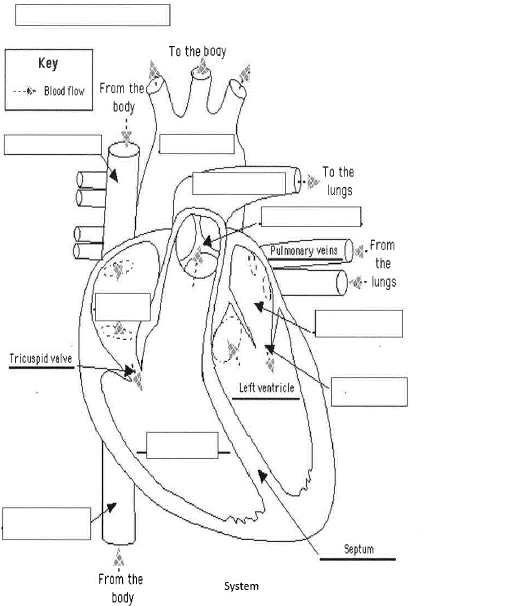
Figure 1: Circulatory System
(Self- labelled)
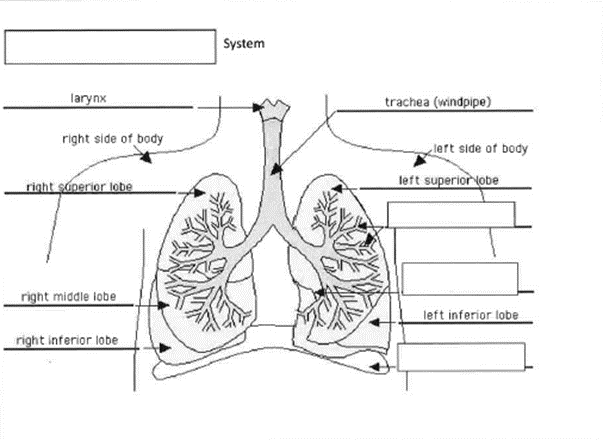
Figure 2: Respiratory System
(Self-Labelled)
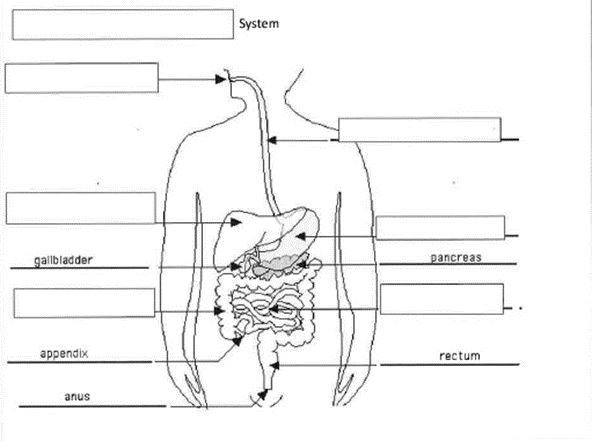
Figure 3: Digestive System
(Self-Labelled)
3. Explain the function of the Cardiovascular, Respiratory, and Digestive systems
The stomach, lungs, and heart being the parts of the cardiovascular system should be maintained healthy to help maintain the rest of the body healthy (Mitchell et al., 2021). These include the heart and blood vessels which a system that are responsible for transferring blood all over the body in the process of elimination, feeding, and oxygenating (Mitchell et al., 2021).
Blood is circulated through a network of tubes, namely blood vessels; veins, arteries, and capillaries, to deliver oxygen and nutrients to the tissues and remove waste products such as carbon dioxide from them.
Lungs, the muscles of respiration, and the respiratory tract are all together known as the respiratory system (Santacroce et al., 2021).
It also makes it possible to interconvert carbon dioxide to its surrounding external surroundings and oxygen to the body (Santacroce et al., 2021). Air is inhaled from either the mouth or the nose then gets to the trachea and then to the lungs where carbon dioxide is expelled and oxygen is picked up in the blood.
The digestive system also known as the alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract is the process of breaking down food into forms that can be utilized for growth, replacement of worn-out tissues, or for energy sources (Wong et al., 2020).
It is comprised of the mouth, the oesophagus, the stomach, small intestines, and the large intestines and other organs that accompany it including the pancreas and liver (Wong et al., 2020). In addition, it eliminates such garbage that cannot be digested at all. Altogether, these systems ensure that the body is well-functioning and support overall health.
4. Describe the body systems below and explain the structure and function of each with diagrams.
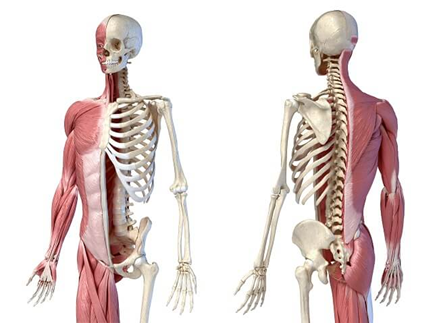
Figure 4: Musculoskeletal System
(Source: biologydictionary.net, 2024)
Structure: The musculoskeletal system is made up of skeletal system bones, muscles and tendons, and ligaments that connect the bones to the muscles (Mukund & Subramaniam, 2020). The skeletal system gives support as well as affords protection to the essential organs while the muscular work to move the body parts and offer strength.
Function: It provides a structural base in the body, helps in muscular contractions, and also shields vital organs within the body. Skeletal muscles are connected to the bones with the help of tendons; examples of such movements are walking or running (Mukund & Subramaniam, 2020). Also, bones are mineralized structures containing calcium and phosphorus which are vital in metabolism and blood synthesis.
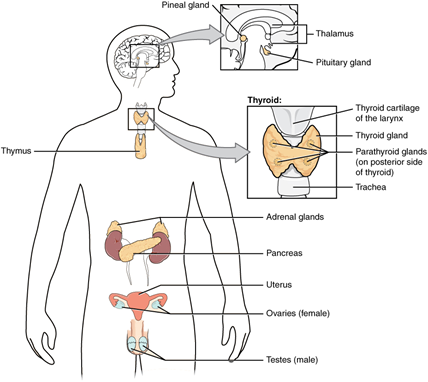
Figure 5: Endocrine System
(Source: louis.pressbooks.pub, 2024)
Structure: The endocrine system involves glands including the pituitary gland, thyroid gland, adrenal gland, and the pancreas, and hormones are released in the bloodstream (Purslow, 2020).
Function: It is involved in how the body’s many processes work and coordinate the body and its systems to achieve balance, or homeostasis, through the secretion of hormones that act on metabolism, growth, and sexual, or emotional functions (Purslow, 2020). It circulates in blood to reach its target organs and glands affecting several activities in the body including energy metabolism, sleep, or stress.
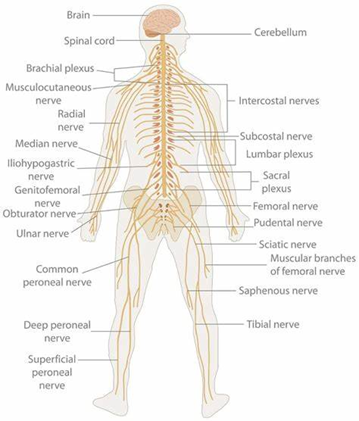
Figure 6: Nervous System
(Source: biologydictionary.net, 2024)
Structure:
The nervous system incorporates the brain, spinal cord, and nerves. The head is the control center of the human body, the nerve is dispersed in the human body and transmits information (Jorgenson et al., 2020).
Function:
It integrates the activities that occur in the body either as a result of desire or force in the form of reflex arc, is involved in the reception of stimuli, processing of such stimuli then in return sending signals to muscles and glands. The simplest functions within an organism, including the ability to breathe, the rate of one’s heart, as well as the capacity to digest food, are controlled by the nervous system (Jorgenson et al., 2020). This element also has a significant impact on cognition, memory, and emotions.
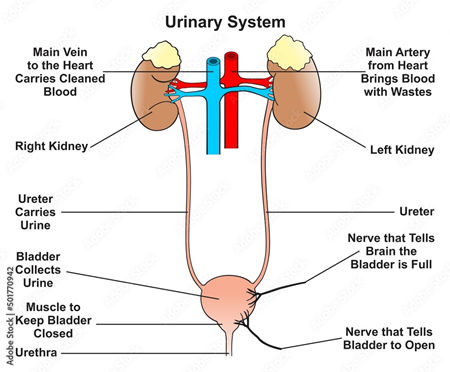
Figure 7: Urinary System
(Source: bajeczneobrazy.pl, 2024)
Structure: The urinary system consists of kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra; it is thoroughly involved in filtering waste products from the blood in the form of urine (Teixeira et al., 2020).
Function: It maintains water and electrolyte concentration, and the pH of blood by filtering blood and getting rid of water, salts, and waste products (Teixeira et al., 2020). They also synthesize hormones involved in the regulation of blood pressure and the levels of red blood cells in the body.
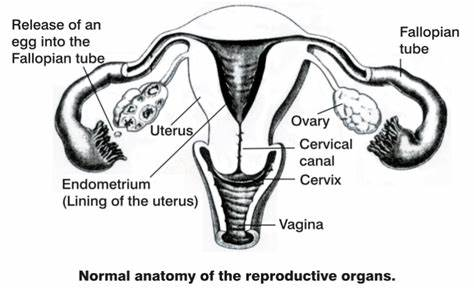
Figure 8: Female Reproductive System
(Source: womensultrasound.com.au, 2024)
Structure: The reproductive system varies between males and females. In males it has testis, epididymis, vasa deferentia or ductus epididymis, and penis. In females, it also consists of ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, vagina, and breasts (Thyfault & Bergouignan, 2020).
Function: It provides for reproduction for the generation of offspring and young ones. In males, it involves the production and release of sperm. In females, it creates ova, entails fetal development during pregnancy, and synthesizes breast milk in the female body (Thyfault & Bergouignan, 2020).
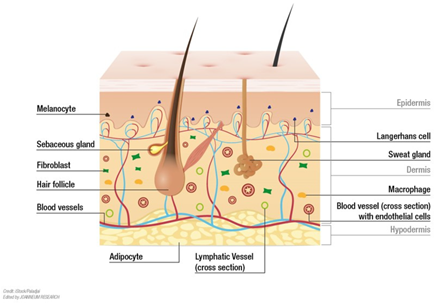
Figure 9: Integumentary System
(Source: researchgate.net, 2023)
Structure: The integumentary system encompasses the skin, hair, nails, sweat, and oil glands.
Function: It plays the important role of a shield against impurities and infections, bacteria, and even UV light (Stogios et al., 2021). The skin has functions of cooling and insulating the body through sweating. Hair and nails perform the extra tasks of protection and mechanosensation.
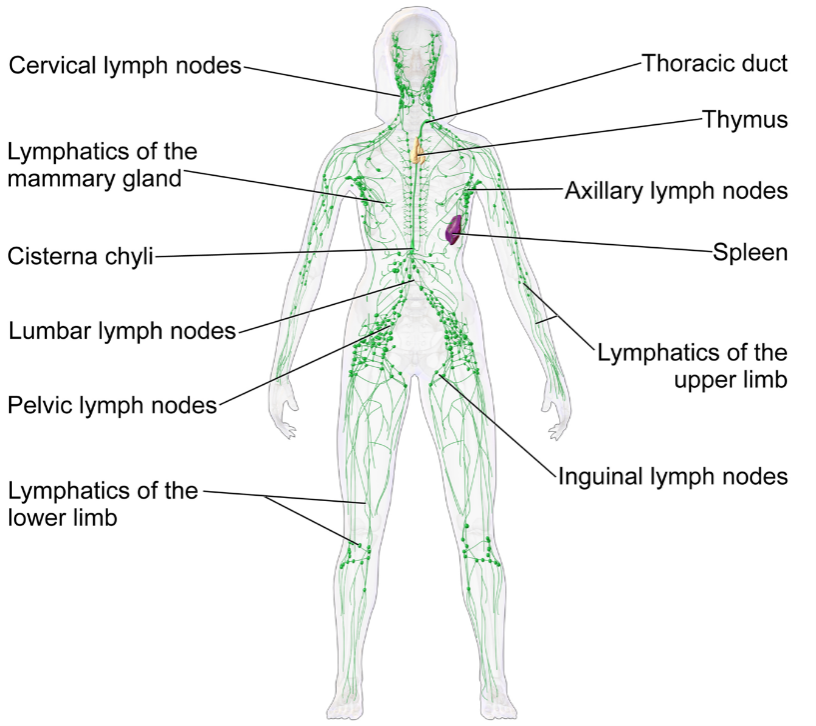
Figure 10: Lymphatic System
(Source: bio.libretexts.org, 2024)
The parts of the Lymphatic System include Lymph Nodes, Lymphatic Vessels, Spleen, Thymus, and Tonsils (Stogios et al., 2021).
In maintaining the body’s immune defense this transports lymphatic fluids, white blood cells, and antibodies throughout the body (Teufel & Fletcher, 2020). The lymphatic system opposes germs and poisons, controls isotonicity, and absorbs fats from the small intestines.
5. List the common medical check-ups people should have (Including gender-specific, age, and frequency)
Primary care check-ups include a complete medical profile examination. Healthy adults should have a physical examination every 5 years if they are below 45 years of age, while for those who are from 45 to 65, it is recommended that they have the examination every two years and annually for those over 65 years of age (Hidaka et al., 2020).
Regular dental checkups should be made every 6-12 months, though smokers should attempt to do this twice a year. People should go for eye tests at least twice in two years, or annually if they have diabetes or use spectacles. For colon examinations, patients from 40 years old are given a blood test for faecal occult matter and a colonoscopy after 10 years (Hidaka et al., 2020).
An examination of epididymis and prostate should be done on men at the age of fifty with earlier exploration in case of a family history of the same disease. Screening for melanoma by skin examination should start from age 20 and should done once in two to three years, and once annually after the age of forty. Women should begin getting mammograms at the age of 40 be undergo yearly pelvic examinations and pap smears starting at 18 years of age (Hidaka et al., 2020).
6. Refer to the nurses or medical dictionary and write the meanings of the following medical terminologies.
Diabetes refers to a long-term problem with your body’s ability to process glucose a type of sugar. A few reasons that glucose is essential to your health have classified glucose as a fuel that is crucial for the cells present in the muscles and tissues.
Diabetes is a condition in which your body does not produce the right amount of insulin or cannot function with the insulin produced efficiently (Teufel & Fletcher, 2020).
Insulin is a hormone created by the pancreas, it signals cells to allow glucose for entry and then to be used up as energy. If there is not enough insulin, sugar remains in the blood and causes high levels of blood glucose.
Optometrists are the health care providers who focus on the eyes and vision of the human body. They conduct a complete examination to determine the overall condition of the human eyes; recommend opticians/glasses and contact lenses in cases of vision disorders; diagnose other conditions such as glaucoma and cataracts; treat or recommend clients to other medical personnel respectively (Kalantar et al., 2021).
A colonoscopy is an evaluative medical procedure that aims at inspecting the inner part of the colon and rectum. It is done using a long and bendable tube referred to as a colonoscope; it is fitted with a small camera and light.
During a colonoscopy, the doctor can see the entire surface of the colon and rectum inspecting for possible precancerous growths known as polyps, tumours, inflammation, or irregularities of bleeding (Kalantar et al., 2021).
Melanoma is a malignant neoplasm that arises from melanocytes derived from the neural crest and develops from the skin colour-producing chromophore, melanin. Melanoma can be found anywhere on the body but is predominantly seen in areas that are often exposed to the sun as the face, neck, arms, and legs (Stavropoulou et al., 2021).
High blood pressure, or hypertension, is a condition in which the force of blood against the artery walls is too high for an extended amount of time.
Blood pressure is defined as the pressure by which the blood is circulated by the heart to its volume and the resistance through arteries (Stavropoulou et al., 2021). Blood pressure increases with age and stress levels, thus when the blood pressure is high, the heart compensation rate is also high.
In the context of the present research, an electrocardiogram can be described as a test that measures the electrical activity of the heart over a certain time (Kakitapalli et al., 2020). It supervises the electrical action of the heart stimulating it on the heart muscles and comes up with a record in the form of a graph-like strip called an electrocardiogram.
Cholesterol is defined more as a waxy, fiat-like substance that is part of all the cells in the body. Cholesterol is vitally required in the development of cell membranes, the synthesis of hormones such as estrogen and testosterone, and the production of vitamin D or the active form (Kakitapalli et al., 2020). Cholesterol however is transported in the blood as lipoproteins particularly the LDL and the HDL.
It is a film of the mammary gland done through X-ray in the screening and identification of breast cancer. It can detect breast cancer or some anomaly in the breast tissue that cannot be seen by the naked eye or is too small to palpate from the surface of the breast (Hakim & Pertiwi, 2023).
Osteoporosis is a bone disease that is characterized by weak and thin bones and is usually accompanied by an increasing frequency of fractures, especially in the vertebral region, hips, and wrists (Hakim & Pertiwi, 2023). Osteoporosis on the other hand is a disease whereby the body's formation of bones is surpassed by the rate at which it breaks down bones and leads to frail bones.
Pneumonia can be defined as an illness that results in inflammation of the air-filled tiny sacs in a lung or both lungs. This leads to the accumulation of fluid or pus in the air sacs with the production of phlegm and /or pus, increased body temperature body aches, shivering, and shortness of breath (Harris & Grice, 2022). The contraction of pneumonia stems from infections that are caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, or even parasitic organisms.
7. Explain the basic structures and functions of cells tissues and organs, including diagrams as required.
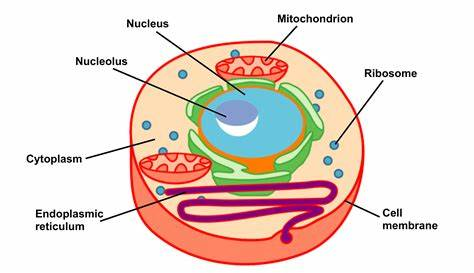
Figure 11: Cell Structure and Function
(Source: medicalexamprep.co.uk, 2020)
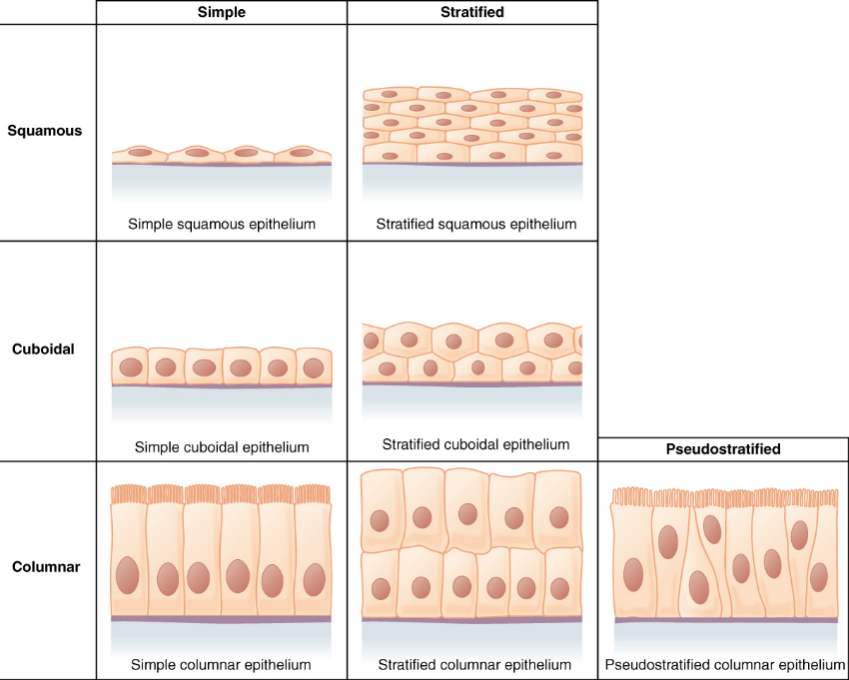
Figure 12: Tissues Structure and Function
(Source: pressbooks.bccampus.ca, 2024)
They are the structural and internal components of living organisms that are also capable of carrying out specialized actions. Tissues are collections of cells that have similar natures and functions in performing certain activities (Harris & Grice, 2022).
Organs consist of tissues of various variations referred to as organs and are more organized structures performing unique functions, for instance, the heart and lungs. Hence, cells, tissues, and organs act as systems that help maintain homeostasis as well as perform physiological functions in the body.
1. Explain how the below maintain a healthy body:
Physical exercise as part of systematic physical education is an important factor that helps to sustain cardiovascular, muscles, and flexibility. It plays a role in weight management, prevention of chronic illnesses, such as cardiovascular diseases and type 2 diabetes, and boosting mood and mental state (O'Donoghue et al., 2021). Exercise also helps in a good flow of blood in the body, thus oxygen and nutrients are allowed to flow in the body properly.
Another significant aspect is that a healthy diet with the intake of all the necessary nutrients is of vital importance. In this way, vitamins, minerals, proteins, carbohydrates, fats, and fibre required for the proper functioning of the body are also obtained. Consequently, a diet that has fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein, and healthy fats is necessary for bodily processes, building up an immunity level, and preventing detrimental diseases inclined to make an individual overweight (O'Donoghue et al., 2021).
Sweating produces cooling, shivering to warm the body, and regulating blood flow to cool or warm the body (Su et al., 2020). This regulation is vital for enzyme activity and then the overall function of cells in an organism’s body. Body temperature modulation means that significant organs and tissues are smoothly running; and avoiding heat stress or low temperatures.
Individual’s blood pressure should therefore be regulated for better Circulatory system health since blood circulation through arteries and veins is effective in delivering oxygen and nutrients to body tissues and organs (Schutte et al., 2022).
Normal pressure decreases the workload of the pump and prevents a plethora of cardiovascular diseases, stroke, and renal issues. Other things including dieting, exercising, managing stress, and quitting smoking all have a positive impact on regulating blood pressure.
2. In the following table, explain the purpose of each food type and what foods or other locations it may be obtained from.
| Food type | Purpose | Where it may be obtained |
| Protein |
|
Meat, fish, eggs, milk, milk products, nuts, pulses, legumes, soya etc |
| Carbohydrate |
|
Rice, wheat, bread, fruits, vegetables, cereals, millet, etc |
| Fat |
|
Healthy oils, peanut butter, avocados, nuts, seeds, butter. |
| Vitamin A |
|
Carrots, Sweet potatoes, meat liver, spinach etc. |
| Vitamin Bl (Thiamine) |
|
Whole grains, meat, legumes, seeds, nuts, pulses etc. |
| Vitamin B12 |
|
Meat, fish, milk, milk products, cereals, etc. |
| Vitamin C |
|
Vitamin C-rich fruits, berries, green leafy vegetables. |
| Vitamin D |
|
Sunlight, milk, milk products fatty fish, fish liver oil, egg yolk etc. |
| Vitamin K |
|
Green leafy vegetables, Fish, meat, milk and milk products etc. |
| Sodium |
|
Table salt, Any processed food, soups, green leafy vegetables, etc. |
| Potassium |
|
Bananas are a rich source of potassium, potatoes, spinach, green vegetables, beans, etc. |
| Calcium |
|
Milk and milk products, green leafy vegetables, and fortified foods. |
Table 1: Foods, their purpose, and sources
(Self-Created from Guide)
1. How do all of the major body systems relate to one another?
The human body entails major systems that operate in coordination to support general human health. The blood circulatory system delivers nutrients and oxygen to the cells, with the help of the respiratory system which supplies oxygen and eliminates CO2. The movement of an animal occurs through the circulatory pump, the muscular system, the digestive system for the breakdown of food to produce energy, and the nervous system for the relation of responses.
The endocrine system maintains the hormones of the metabolism and growth. The musculoskeletal system is involved in movement and acts as a protective covering for organs (Su et al., 2020). The disease-fighting mechanism is initiated by the immune system and the lymphatic system aids. Such systems regulate each other’s performance to operate effectively and accommodate internal and external environment nuances.
1. What are the different materials you can use as you share information about the healthy functioning of the body with staff, consumers, and their family members?
When sharing information about healthy body functioning with staff, consumers, and their families, various materials can effectively convey important messages:
1. Brochures and Pamphlets: These are brief and graphical, and therefore help to deliver complicated information to the target group’s awareness (Schutte et al., 2022).
2. Posters and Infographics: Reference materials that are taught and easily accessible by the crews in the general areas of the ship.
3. Videos and Animations: Collaborative media that shows processes in the human body and how to stay healthy (Rounsefell et al., 2020).
4. Educational Workshops: The breakout/proactive sessions where the participants can understand issues more via demonstrations and follow-up discussions.
5. Websites and Online Resources: Seemly sites providing long-reads, Q&As, and files for download.
6. Health Seminars and Webinars: Small group lectures feature experts who present information on selected areas of health and respond to questions from the audience (Rounsefell et al., 2020).
2. State the special senses (smell, taste, vision, equilibrium, and hearing) and their purposes.
The special senses include:
1. Smell (Olfaction): It affects the taste buds, samples chemical alterations in the surrounding environment and results in the creation of various feelings (Cohen et al., 2021).
2. Taste (Gustation): Regarding the chemical aspects, the companies and manufacturers that test the foods and beverages get to identify the sweet, sour, salty, and bitter tastes among others.
3. Vision: One of how the people in the building would employ the part of the brain to get the light and in turn, utilize it to observe and acquire information from the shapes, colors, and distance (Cohen et al., 2021).
4. Equilibrium (Balance): It is involved in median and polar regulation of the body’s position of movement relative to its operating center and also the vestibular system.
These senses in coordination provide vital information concerning the space and support regarding it.
Explain the basic structure and function of the immune system. How does the body protect itself from Infection?
The body's defence mechanism against infections and other dangerous intruders is the immune system (Arasa et al., 2021). It is divided into two primary categories as adaptive immunity and innate immunity. Innate immunity serves as the initial line of defence.
This supplies quick and nonspecific protection. It comprises immune cells like neutrophils and macrophages that engulf and eliminate infections and physical barriers like the skin and mucous membranes.
Adaptive immunity becomes increasingly specialised over time. It involves B and T lymphocytes that identify certain antigens in infections. T cells go straight after infected cells as B cells make antibodies that attach to and neutralise antigens (Helmink et al., 2020).
Immunological memory enables the immune system to produce a quicker and more powerful response following successive exposures to the same pathogen. The immune system ensures the body's survival and well-being through a coordinated series of innate and adaptive immune responses.
1. Explain the fluid and electrolyte balance of the body.
Maintaining the body's optimum balance of electrolytes and fluids is essential for optimal physiological function (Bennet et al., 2021). The equilibrium between fluid intake and outflow is known as fluid balance. It is controlled by the same systems that control hormone levels and thirst as aldosterone and antidiuretic hormone (ADH).
The function of nerves and muscles as fluid balance depend heavily on electrolytes. That includes sodium, potassium, chloride, and bicarbonate (Pourfridoni et al., 2021). Blood pressure and fluid distribution are regulated by sodium. That is the main electrolyte in extracellular fluid. Potassium is mostly present within cells and is essential for both muscle contractions and nerve impulses.
Bicarbonate controls the acid-base balance as chloride maintains pH and balances bodily fluids.
The kidneys play an essential function in maintaining this equilibrium. It adjusts the amount and concentration of urine in accordance with the body's requirements. Dehydration or hyperhydration are examples of imbalances.
This may cause symptoms that range from weariness and thirst to more serious problems including electrolyte imbalances or organ failure (Eaddy & Watene, 2023). Proper hydration and medical treatment as needed are essential for maintaining appropriate fluid and electrolyte balance.
2. Explain the elimination of waste products from the body.
The body has to remove waste materials from itself in order to be healthy. This ensures that all of its systems are operating as bodily systems (Feral, & Massin, 2020). It is mostly concerned with the urinary system and other organs also play an important part.
Urinary System: The kidneys play a major role in getting rid of waste. They filter blood to get rid of extra ions, water, and waste materials as urea and uric acid (Houat et al., 2021). The nephrons in the kidneys combine these filtered wastes with water and electrolytes to make urine.
Digestive System: The digestive tract is also used for the removal of waste. Toxins and metabolic waste products are broken down by the liver and transformed into bile (Sensoy, 2021). That is then expelled into the intestines and finally removed in faeces.
Respiratory System: The lungs' excretion of carbon dioxide during exhalation contributes minimal to the respiratory system.
Skin: The excretion of urea, salts, and water via sweat glands in the skin aids in the disposal of waste.
The accumulation of toxins that might harm cellular function and general health can only be avoided by proper waste removal. Diseases that impair the removal of waste from the body may have a major negative impact on one's health.
Arasa, J., Collado-Diaz, V., & Halin, C. (2021). Structure and immune function of afferent lymphatics and their mechanistic contribution to dendritic cell and T cell trafficking. Cells, 10(5), 1269. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10051269
bajeczneobrazy.pl, (2024). Human urinary system infographic diagram structure and parts including right left kidney ureter nerves bladder muscle urethra blood vein artery urine vector illustration drawing for anatomy biology - obrazy, fototapety, plakaty. Retrieve from: https://www.bajeczneobrazy.pl/obrazy-na-plotnie/human-urinary-system-infographic-diagram-structure-and-parts-including-right-left-kidney-ureter-nerves-bladder-muscle-urethra-blood-vein-artery-urine-vector-illustration-drawing-for-anatomy-biology-501770942. [Retrieved on: 16 July 2024]
Bennet, D., Khorsandian, Y., Pelusi, J., Mirabella, A., Pirrotte, P., & Zenhausern, F. (2021). Molecular and physical technologies for monitoring fluid and electrolyte imbalance: A focus on cancer population. Clinical and translational medicine, 11(6), e461. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdfdirect/10.1002/ctm2.461
bio.libretexts.org, (2024). Lymphatic System. Retrieve from: https://bio.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Human_Biology/Human_Biology_(Wakim_and_Grewal)/20%3A_Immune_System/20.3%3A_Lymphatic_System. [Retrieved on: 16 July 2024]
biologydictionary.net, (2024). Body Systems. Retrieve from: https://biologydictionary.net/body-systems/. [Retrieved on: 16 July 2024]
biologydictionary.net, (2024). Nervous System. Retrieve from: https://biologydictionary.net/nervous-system/. [Retrieved on: 16 July 2024]
Cohen, R., Newton-John, T., & Slater, A. (2021). The case for body positivity on social media: Perspectives on current advances and future directions. Journal of health psychology, 26(13), 2365-2373. https://uwe-repository.worktribe.com/index.php/OutputFile/6560955
Eaddy, N., & Watene, C. (2023). Perioperative management of fluids and electrolytes in children. BJA education, 23(7), 273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjae.2023.03.006
Feral, J. P., & Massin, C. (2020). Digestive systems: holothuroidea. In Echinoderm nutrition (pp. 191-212). CRC Press. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Jean-Pierre-Feral/publication/233883303_Digestive_systems_Holothurioidea/links/0912f510139df4ada0000000/Digestive-systems-Holothurioidea.pdf
Hakim, D. R., & Pertiwi, K. R. (2023). Development of innovative student worksheet using google sites for reproductive system material. Jurnal Penelitian Pendidikan IPA, 9(9), 7484-7490. https://doi.org/10.29303/jppipa.v9i9.4429.
Harris-Tryon, T. A., & Grice, E. A. (2022). Microbiota and maintenance of skin barrier function. Science, 376(6596), 940-945. https://bookcafe.yuntsg.com/ueditor/jsp/upload/file/20220616/1655336118388049433.pdf.
Helmink, B. A., Reddy, S. M., Gao, J., Zhang, S., Basar, R., Thakur, R., ... & Wargo, J. A. (2020). B cells and tertiary lymphoid structures promote immunotherapy response. Nature, 577(7791), 549-555. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-1922-8
Hidaka, T., Kasuga, H., Endo, S., Masuishi, Y., Kakamu, T., Takeda, A., ... & Fukushima, T. (2020). Are lifestyle pattern changes associated to poor subjective sleep quality?: a cross-sectional study by gender among the general Japanese population underwent specified medical check-ups in 2014 and 2015. BMJ open, 10(12), e037613. https://bmjopen.bmj.com/content/bmjopen/10/12/e037613.full.pdf
Houat, A. P., Guimarães, C. T., Takahashi, M. S., Rodi, G. P., Gasparetto, T. P., Blasbalg, R., & Velloni, F. G. (2021). Congenital anomalies of the upper urinary tract: a comprehensive review. Radiographics, 41(2), 462-486. https://pubs.rsna.org/doi/pdf/10.1148/rg.2021200078
Jorgenson, K. W., Phillips, S. M., & Hornberger, T. A. (2020). Identifying the structural adaptations that drive the mechanical load-induced growth of skeletal muscle: a scoping review. Cells, 9(7), 1658. https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4409/9/7/1658/pdf.
Kakitapalli, Y., Ampolu, J., Madasu, S. D., & Sai Kumar, M. L. S. (2020). Detailed review of chronic kidney disease. Kidney Diseases, 6(2), 85-91 https://karger.com/kdd/article-pdf/6/2/85/3055842/000504622.pdf.
Kalantar-Zadeh, K., Jafar, T. H., Nitsch, D., Neuen, B. L., & Perkovic, V. (2021). Chronic kidney disease. The lancet, 398(10302), 786-802. https://doi.org/10.1016/ S0140-6736(21)00519-5.
louis.pressbooks.pub, (2024). BASIC ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY OF THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM. Retrieve from: https://louis.pressbooks.pub/medicalterminology/chapter/endocrine-anatomy-physiology/. [Retrieved on: 16 July 2024]
medicalexamprep.co.uk, (2020). Cell Structure and Function Part 1 – The Organelles. Retrieve from: https://www.medicalexamprep.co.uk/cell-structure-and-function-part-1-the-organelles/. [Retrieved on: 16 July 2024]
Mitchell, J. A., Kirkby, N. S., Ahmetaj-Shala, B., Armstrong, P. C., Crescente, M., Ferreira, P., ... & Warner, T. D. (2021). Cyclooxygenases and the cardiovascular system. Pharmacology & therapeutics, 217, 107624. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2020.107624
Mukund, K., & Subramaniam, S. (2020). Skeletal muscle: A review of molecular structure and function, in health and disease. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Systems Biology and Medicine, 12(1), e1462. https://doi.org/10.1002/wsbm.1462.
O'Donoghue, G., Blake, C., Cunningham, C., Lennon, O., & Perrotta, C. (2021). What exercise prescription is optimal to improve body composition and cardiorespiratory fitness in adults living with obesity? A network meta‐analysis. Obesity Reviews, 22(2), e13137. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1111/obr.13137
Pourfridoni, M., Abbasnia, S. M., Shafaei, F., Razaviyan, J., & Heidari-Soureshjani, R. (2021). Fluid and electrolyte disturbances in COVID‐19 and their complications. BioMed Research International, 2021(1), 6667047. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/6667047
pressbooks.bccampus.ca, (2024). Tissue Structure and Functions. Retrieve from: https://pressbooks.bccampus.ca/dcbiol110311092nded/chapter/unit-6-tissue-structure-and-functions/. [Retrieved on: 16 July 2024]
Purslow, P. P. (2020). The structure and role of intramuscular connective tissue in muscle function. Frontiers in Physiology, 11, 495. https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/physiology/articles/10.3389/fphys.2020.00495/pdf.
researchgate.net, (2023). Modelling the Complexity of Human Skin In Vitro. Retrieve from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Structural-details-of-human-skin-The-skin-is-composed-of-three-distinct-layers-the_fig1_369057462. [Retrieved on: 16 July 2024]
Rounsefell, K., Gibson, S., McLean, S., Blair, M., Molenaar, A., Brennan, L., ... & McCaffrey, T. A. (2020). Social media, body image and food choices in healthy young adults: A mixed methods systematic review. Nutrition & Dietetics, 77(1), 19-40. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdfdirect/10.1111/1747-0080.12581
Santacroce, L., Charitos, I. A., Ballini, A., Inchingolo, F., Luperto, P., De Nitto, E., & Topi, S. (2020). The human respiratory system and its microbiome at a glimpse. Biology, 9(10), 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9100318
Schutte, A. E., Kollias, A., & Stergiou, G. S. (2022). Blood pressure and its variability: classic and novel measurement techniques. Nature Reviews Cardiology, 19(10), 643-654. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41569-022-00690-0.pdf.
Sensoy, I. (2021). A review on the food digestion in the digestive tract and the used in vitro models. Current research in food science, 4, 308-319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crfs.2021.04.004
Stavropoulou, E., Kantartzi, K., Tsigalou, C., Konstantinidis, T., Romanidou, G., Voidarou, C., & Bezirtzoglou, E. (2021). Focus on the gut–kidney axis in health and disease. Frontiers in Medicine, 7, 620102. https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmed.2020.620102/pdf.
Stogios, N., Gdanski, A., Gerretsen, P., Chintoh, A. F., Graff-Guerrero, A., Rajji, T. K., ... & Agarwal, S. M. (2021). Autonomic nervous system dysfunction in schizophrenia: impact on cognitive and metabolic health. npj Schizophrenia, 7(1), 22. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41537-021-00151-6.
Su, Y., Ma, C., Chen, J., Wu, H., Luo, W., Peng, Y., ... & Li, H. (2020). Printable, highly sensitive flexible temperature sensors for human body temperature monitoring: a review. Nanoscale Research Letters, 15, 1-34. https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1186/s11671-020-03428-4.pdf.
Teixeira, P. D. F. D. S., Dos Santos, P. B., & Pazos-Moura, C. C. (2020). The role of thyroid hormone in metabolism and metabolic syndrome. Therapeutic advances in endocrinology and metabolism, 11, 2042018820917869. https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/2042018820917869.
Teufel, C., & Fletcher, P. C. (2020). Forms of prediction in the nervous system. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 21(4), 231-242. https://orca.cardiff.ac.uk/id/eprint/129285/1/Fletcher_fig+legend+edits2.pdf.
Thyfault, J. P., & Bergouignan, A. (2020). Exercise and metabolic health: beyond skeletal muscle. Diabetologia, 63(8), 1464-1474. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-020-05177-6.
womensultrasound.com.au, (2024). Women's Ultrasound Melbourne. Retrieve from: https://womensultrasound.com.au/services/female-reproductive-diagram/. [Retrieved on: 16 July 2024]
Wong, S. H., Lui, R. N., & Sung, J. J. (2020). Covid‐19 and the digestive system. Journal of gastroenterology and hepatology, 35(5), 744-748. https://doi.org/10.1111/jgh.15047
Are you confident that you will achieve the grade? Our best Expert will help you improve your grade
Order Now