$20 Bonus + 25% OFF CLAIM OFFER
Place Your Order With Us Today And Go Stress-Free
The study of microbes, organisms that are too small to be seen with the naked eye is Microbiology. Before emerging as a branch of biology, microbiology enjoyed its applications in human life in the form of fermented foods.
Recent evidence from archaeology suggests that alcoholic beverages from fruits, honey, and rice, were made in Neolithic China as early as 7000 B.C. The principle that makes fermented food, a savouring is, fermentation, the metabolism in microbes. Microbes are also detrimental to humans and other animals as they cause diseases in them.
Thus, microbes remained undisclosed frenemies of human life from the early civilizations.
Important periods in Microbiology:
(1665 – 83) - Antoni Von Leeuwenhoek and Robert Koch – aided with Microscopy - Discovery of Microbes.
(1857 – 1914) – Emergence of Microbiology as a separate domain in Biology with key scientific discoveries by Louis Pasteur and Robert Koch – Golden Age of Microbiology.
(1928 – present) – Modern Era of Microbiology - Integration of Microbiology with disciplines Molecular Biology, Recombinant DNA technology and Genetics.
The following are the areas where the celebrated status of integrated Microbiology assumes a pivotal role:
Health Industry: Vaccines, steroids, antibodies, antibiotics, vitamins, probiotics, enzymes, and therapeutics are the major areas where microbiology finds its applications. Studying microbes helps detect, cure, and prevent diseases.
Food and Dairy Industry: Cheese, curd, yogurt, bread, vinegar, butter, fermented beverages, etc, are multi-million industries that rely on microbes.
Agriculture: Microbes decompose and operate the Biogeochemical cycles. They enrich the soil quality. Used as Biofertilizers and Bio-control agents, etc.
Cosmetic Industry: Microbes are the structural and functional hubs for millions of cosmetic products.
Biofuels and Bio-electronics Industry: The metabolism of microbes is amplified to a large-scale level to produce fuels from dead living waste and also biosensors Recent advances are also witnessed in the production of computers.
Water Industry: Wastewater management with microbial cultures ensures the safe release of water into the streams.
The above key areas are enough to justify the importance of studying Microbiology. Microbiology Assignment Help provides a foundation to help Australian students from the basics to ongoing advanced research topics in Microbiology.
Microbiology Assignment Help glorifies the importance of Microbiology and its relevance in human contexts, it also provides help with the various branches of biology.
Botany is the scientific study of plant life. The study includes geographical distribution, classification, structural and physiological aspects of plants.
It is the scientific study of animal life. The study includes geographical distribution, classification, structural, physiological, and behavioural aspects of animals.Get help with the zoology assignment writing service.
Study of the internal structure of living organisms, especially revealed upon dissection.
Cell Biology is the study of the structure, function, and behaviour of cells.
It is a combination of Biology and chemistry. It deals with the chemistry of living organisms and the metabolism that drives the living state of an organism. Read more on Biochemistry Assignment Help.
The branch of science that deals with acellular microbes, is the Viruses. Get help from our virology assignment help.
It deals with the synthesis, interaction, structural and functional aspects of living molecules (Proteins, Carbohydrates, lipids, and Nucleic acids).
The branch of medical biology, that studies the Immune system. Get benefit from our immunology assignment help.
The modern branch of biology dedicated to the study of genes. The study includes structure, function, evolution, and mapping of genes.
Also Read - Biotechnology Assignment Help
Microbiology includes the study of all the microbes smaller than micrometres.
The various microbes studied under the heading microbiology include:
Prokaryotic Microbes: Microbes without a distinct nucleus. Bacteria and Archaea are prokaryotic microbes.
Eukaryotic Microbes: Microbes with a distinct nucleus. Protists (algae and protozoa) fungi and helminths. Though helminths are visible to the naked eye, their lifecycle includes inconspicuous eggs and larvae.
Acellular Microbes: Not cells but macromolecules, made of Proteins and nucleic acids behave as obligate parasites. Viruses are acellular microbes.
Microbiology is vast and includes the following sub-branches:
Pure Microbiology and
Applied Microbiology
Pure Microbiology: The study of biology, classification, distribution, and evolution of Microbes. There are many aspects to it.
Bacteriology: Study of Bacteria.
Virology: Study of Viruses.
Mycology: Study of Fungi.
Protozoology: Study of Protozoans.
Parasitology: Study of helminths and other parasites.
Phycology: Study of algae.
Microbial Genetics: Study of genes, their organization and role in the functioning of a microbe.
Microbial Ecology: Study of the relationship between microbes and their environment.
Evolutionary Microbiology: Study of the evolution of microbes, which also includes classification based on genetic data.
2. Applied Microbiology: It deals with the practical applications of microbes to mankind. This includes the following:
Medical Microbiology: Study and role of pathogenic microbes in human illness. This gives us the potential to detect, cure and prevent diseases. Probiotics in microbiology are assuming their importance in boosting human health.
Food Microbiology: Applications that slow down food spoilage by microbes and the production of fermented foods.
Industrial Microbiology: Exploiting the microbial metabolism at the industrial levels. This includes industrial fermentation, brewing, waste-water treatment, paper recycling, etc.
Agricultural Microbiology: Study of Interactions of microbes with plants and soil. The applications of useful interactions to increase the yield.
Biotechnology: The genetic engineering and culture of microbes at the industrial level to obtain desired products from microbes.
Finding difficulties with the complex topics of Microbiology? Are you looking for assistance with your assignments? Contact us, we shall handle your assignments with utmost excellence.
An advanced topic that our experts made easy for you to understand:
Cell wall in Bacteria: The cell wall in bacteria is the outermost covering, that protects the bacteria from harsh environments. The major component unique to the bacterial cell wall is Peptidoglycan (murein).Structurally murein resembles a meshwork.
Peptidoglycan is also a mesh of glycan chains. Each chain of mesh is made of alternating molecules of NAM (N – Acetyl Muramic acid) and NAG (N – Acetyl Glucosamine).
NAM has 4-5 amino acids linked to it. NAG has no amino acids linked.

NAM of one glycan chain crosslinks with NAM of another glycan chain.
There is a difference in the crosslinks of Gram-Negative and Gram-Positive Bacteria.
| Gram-Positive | Gram-Negative |
| Chains are crosslinked by pentapeptide | Chains are not cross linked |
Cell wall structure in bacteria is of two common types.
| Gram-Positive | Gram-Negative |
| Many layers of Peptidoglycan, very thick. | Thin layer of Peptidoglycan layer |
| 30-100 nanometres thick | 4 nm thick |
| Teichoic acid chains extend through and beyond the peptidoglycan layer. | No Teichoic acid chains. |
| Cell wall is exterior to the plasma membrane | Cell wall is complex and arranged into three layers. Inner Membrane Thin layer of peptidoglycan Outer Membrane |
Same name but different strains:
The thing that we most often see in Microbiology is the name of the strain. There are sightings in Microbiology, where we see the same name of species, with slight modifications that accommodate strain names.
For example, E. coli is a species. Species in microbiology include all those strains, which have a common origin and are more similar to each other than they are to any other strains.
At the biological level, E. coli is a reproductive unit and contains many strains.
Strain is a sub-ordinate to sub-species; however, we don’t use the term sub-species for microbes. Sub-species is a concept that includes individuals of a species isolated by geographical boundaries but can breed if the geographical boundaries are removed.
A strain is usually made from a single isolated colony from a pure culture. Strains can be distinguished from the same species by looking at the phenotypic or genotypic characteristics or both. Strains do not remain the same and change due to accumulating mutations.
Recent evidence from Genomics suggests that strains do not differ in Genomes, but they do in Genes. A strain is different from other strains of the same species, is due to the differences in genes between them. The entire genome almost remains the same.
The following are the strains of E. coli:
1. coli K.12 (Non -pathogenic laboratory strain)
2. coli O157:H7 (Pathogenic – Cause abdominal cramps and diarrhoea)
Also Read - University Of Sydney Assignment Help
Viruses, the acellular Microbes:
Viruses are acellular structures. A – without and Cellular – Cell structures.
The following are the reasons for calling viruses as acellular structures.
They do not contain a cell wall
They do not have a cytoplasm.
No cell organelles.
No respiration
They are just Nucleic acids (DNA or RNA) enclosed in a proteinaceous coat (capsid). Viruses cause a range of diseases in organisms. This makes them sometimes to be called as infectious molecular agents, which is an aspect of non-living things.
The only living feature viruses exhibit is Reproduction. They start reproducing in millions once they enter the living organism. This makes them to be called as Obligate parasites, i.e., they can only be living, inside an organism.
Viruses, thus, lie in between the living and non-living worlds.
Shapes of Bacteria:
Bacteria come in different shapes. Though there are plenty of bacteria, all of them could be categorised into a handful of groups, based on common morphology.
| Name | Description | Image |
| Coccus (pl: Cocci) |
Round |  |
| Bacillus (pl: Bacilli) |
Rod | 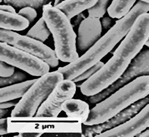 |
| Vibrio (pl: Vibrios) |
Curved Rod | 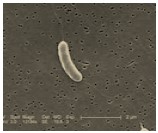 |
| Spirillum (pl: Spirilla) |
Spiral, rigid, with external flagella |  |
| Spirochaete (pl: Spirochaetes) |
Long, flexible, helical spiral, with internal flagella |  |
Are you finding it hard with the scientific jargon and concepts of microbiology? Look at us. Our experts help you master the subject. With their profound knowledge and expertise, they have guided many Australian students ace the concepts of Microbiology.
Jennifer, MSc Microbiology(H) is our academic expert with 7 years of experience. Jennifer excels in basic to advanced knowledge in Microbiology. She will guide you through the toughest parts of microbiology and acquaint you with the subject in an engaging manner. Learn tips and tricks to remember the concepts from her.
Anna is our Microbiology content writer in our organization. Anna's commitment is beyond your classroom success. She provides you with application-oriented problems that you encounter in real-life situations.
Don’t let this opportunity go, take assistance from learned professionals and experts in Microbiology Assignment Help.
Also Read - Assignment Help Perth
Strengthen your knowledge in microbiology by practice. Practice on our free sample papers that expose you to exam-style questions. This increases your confidence. Our site offers you high-quality, downloadable, sample papers, designed to match your academic interests.
Also Read - Research Proposal On Telehealth for Mental Health In UK
Here are the following tips one must have in one’s mind’s eye while writing for an effective microbiology assignment.
Understand the Assignment: Read the assignment instructions carefully. Make note of all the requirements. Identify the key factors to highlight in your assignment.
Collect the Information: Refer to standard books and lecture notes. Browse through websites to get the information related to the assignment in question. Collect much information on the key factors.
Make a Body: Making a body/outline of your assignment will save you time. Note down the headings and break them further into sub-headings, if necessary.
Include Figures: Assignments should include photographs, tables, diagrams, and all other illustrations, wherever necessary. Figures should be numbered and have a title and a legend, which makes data interpretation easier.
Conclusion: The closing paragraph should briefly talk about the summary of the entire work.
Referencing: An assignment should be well-cited with references. The information collected and presented should be supported by their sources of information Failing to do so, will question the content's authenticity. If you face any difficulty or are very new to this, please reach us out.
Proofread and Edit: Last but not least, review your assignment for any errors or inconsistencies. Make necessary revisions to improve the clarity of your work and look for grammatical errors.
Is it challenging for you to understand the concepts of Microbiology? We can help you with it.
The following reasons explain why you should choose us for Microbiology Assignment Help.
Expert Assistance: We are a team of experienced researchers and authors who are well-versed in Microbiology. We have mastered the subject and its applications.
Customized Approach: Student-friendly approach that strikes harmony with their learning paces.
Crystal Clear Concepts: Be it Microbiology or any other discipline of biology, the whole secret lies in mastering the concept. Our experienced tutors are masters at disclosing the concepts.
Timely Delivery: We deliver assignments on time to give you much time for review and submission.
Confidentiality and Privacy: Your privacy is safeguarded by our highly protected systems and networks.
Affordable Pricing: We offer plans much lower than the market value keeping in view the financial plight of students..

Done Masters in Biology from the Charles Sturt University. I have worked as biology teacher for...
Masters in Biology
I have a Master's degree in Electrical and Electronics Engineering and have been working as an onl...
Masters in Electrical Engg
I have an MSc in Economics from the University of Victoria, which I completed in 2011. For the ...
MSc in Economics
Graduated from The University of Sydney with a Masters in Marketing Research. For the first fiv...
Masters in Marketing Research
My name is Sophia Sampson, and I recently earned a Ph.D. in medical science. In addition to be...
Ph.D in Medical Science
Find Best Experts in City wise
Our Best Assignment Help Expert team work.









